Bridging Gaps, Improving Lives


We commit to improve the lives of Filipinos in a meaningful and lasting way. We do this following clearly defined pathways—access and inclusivity, productivity and competitiveness, responsible growth and innovation—towards 2030 mapped in the Ayala Sustainability Blueprint.
We align our desire to bridge societal gaps with the UN Sustainable Development Goals with the blueprint as a guide, valuing potential, reinventing businesses, and transforming communities.
With this Integrated Report, we recognize the business units, our champions, and their respective SDG targets as we continue to address marginalization, untapped potential, and irresponsible growth issues. We review each champion’s strategies every two to three years to ensure relevance considering game-changing technologies and innovations, evolving needs, and complex situations in today’s customer-centered business world.
Building on the gains of being leaders in the field, incubating businesses that make up a resilient portfolio, and strengthening a risk-aware culture will accelerate our growth into a future-ready Ayala Corporation.
ACCESS & INCLUSIVITY

Ayala Foundation, Inc. (AFI)
Target:
To support anti-poverty frameworks resulting in 50 percent reduction of extreme poverty in AFI project areas
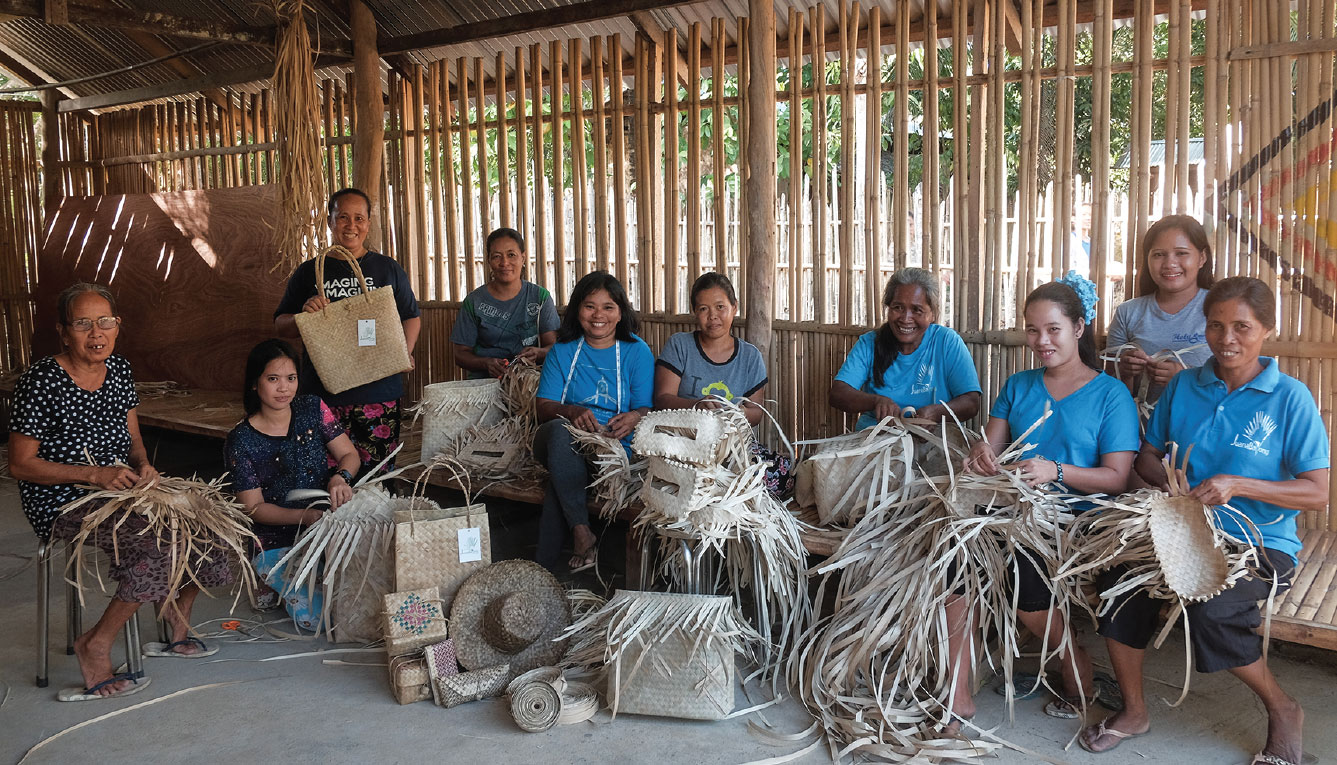

Ayala Foundation works with Lio Sibaltan weavers.
Sixteen percent of Filipinos are considered poor and not able to meet their basic needs despite a growing Philippine economy3.
Poverty unreasonably limits the ability of people to contribute to a stable economy and society, which is necessary to sustain our growth as a business and the development of our country.
Through Ayala Foundation, we work to address extreme poverty especially in communities surrounding our areas of operations. We employ a holistic approach in designing and implementing our programs, from capacity building for our beneficiaries, to making products of value, and to finding them the markets to realize economic gains of their efforts.
Ayala Foundation became the first organization to receive a Social Value Certificate, following a stringent two-year examination process. This proves that their approach to deliver social value meet international standards.
Below are three highlight programs that have been effective in poverty allevation:
El Nido Community Development Program
This was designed to enable communities to better participate and access opportunities in the booming economy of El Nido, Palawan.
We partnered with businesses, local government, and community folk to implement nine livelihood projects including vegetable farming, tricycle operations, traditional weaving, and cashew nuts and cocoa production.
We worked with educational institutions to provide senior high school students on-the-job training opportunities in the hospitality industry to boost their employability upon graduation. We also held job fairs to make it easier for job seekers to access employment opportunities in our properties in El Nido. During disaster emergencies, such as the flood in 2018, we supported affected families by providing relief packages, medical assistance, and repair kits.
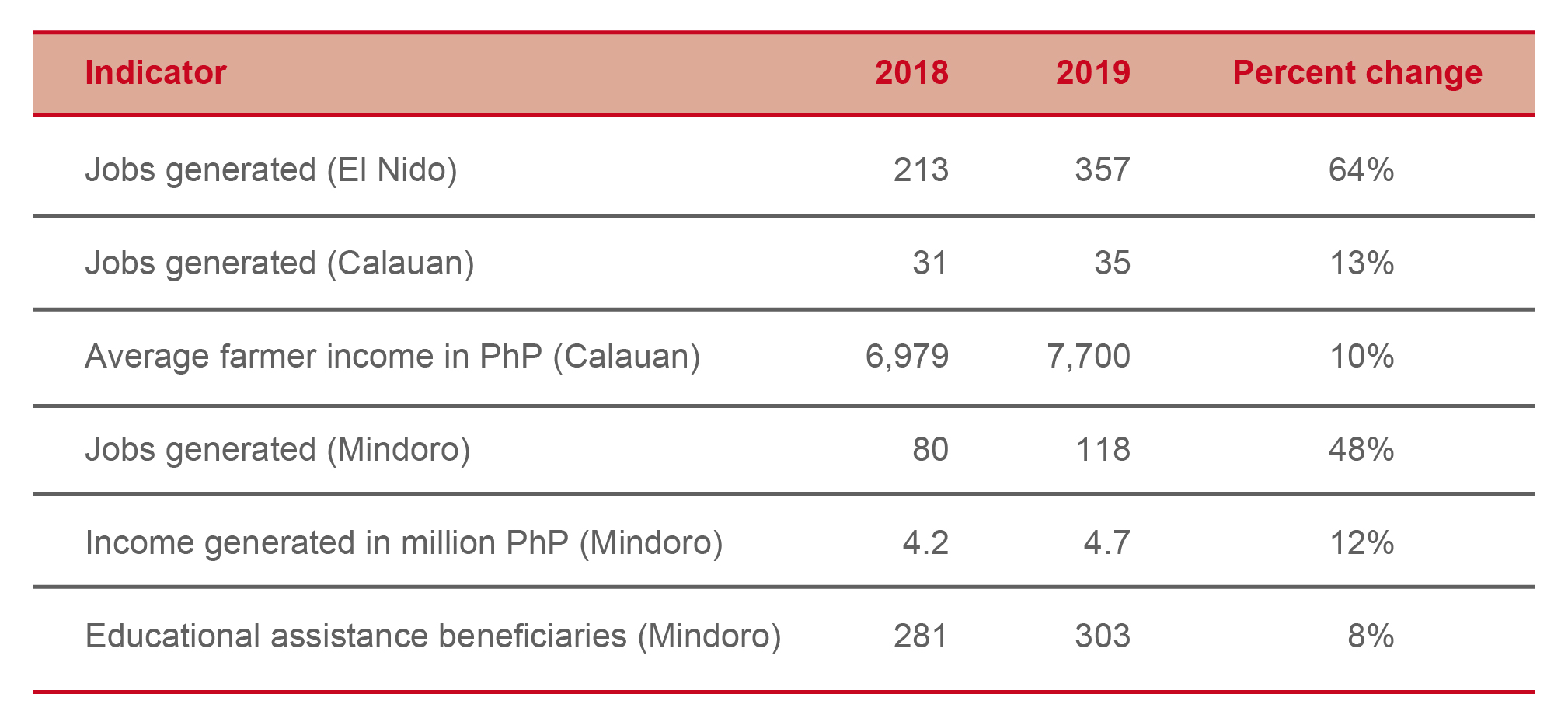
We assessed the effectiveness of our interventions using the Social Return on Investment (SROI) methodology. Our finding showed that the economic value created for our beneficiaries is 26 times more than the funds we spent on the projects.
MDC Greens Ornamental Farm
This project targeted families relocated to Calauan, Laguna who were victims of Typhoon Ondoy in 2009, and those displaced by the Pasig River Rehabilitation Program. We trained our beneficiaries on farming to enable them to grow ornamental plants and organized them into a cooperative. Their 35-member cooperative now runs a five-hectare ornamental plant farm that supplies Makati Development Corporation’s landscape projects.
This year, we have realized a 10 percent increase of their income to ₱7,700 per month. We continue to assist the community to bring their project to scale by linking to more markets to ultimately bring them out of poverty.
Iraya-Mangyan Development Program
The project for the indigenous community in Puerto Galera, Oriental Mindoro focused on skills training and education. Ayala Foundation worked with the community to preserve its weaving tradition while generating economic benefits for themselves. The beneficiaries were enabled to produce woven nito products, accessories, and beaded bags. They were also trained to offer eco-cultural tour guiding services. These activities generated approximately ₱4.7 million in 2019 and ₱4.2 million in 2018. The Iraya-Mangyan beneficiaries received ₱1.6 million out of the total earnings in 2019. The program generated 118 jobs in 2019, a 48 percent increase from 2018.
Additional support we provided the community were: educational assistance to 303 students, feeding programs for 281 students, and free medical consultations to 6,790 patients.
We see how these three community programs have improved the lives of our beneficiaries. Ayala Foundation’s SROI study showed that these are highly effective models for creating social value and addressing poverty. We continue to look into opportunities to replicate these models in more areas where we have market presence.
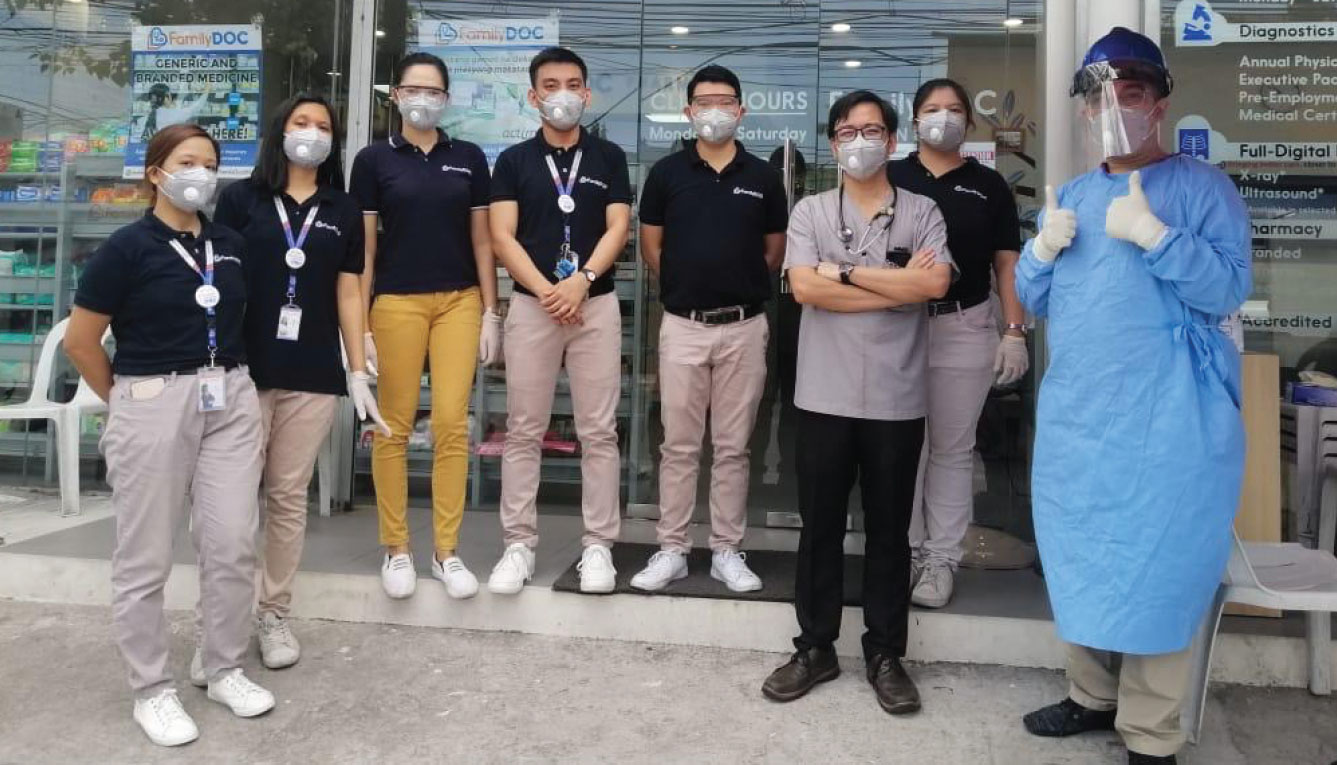

AC Health employees as frontliners in the Covid-19 pandemic.
Out of pocket health expenses by Filipinos increased by 10.5 percent4, making access to healthcare products and services difficult. This condition may be improved by the Universal Health Coverage (UHC) Law, which automatically enrolls all Filipinos to the National Health Insurance Program. However, the current state of the national health system is seen to experience challenges to accommodate a potentially bigger demand.
A healthy population is essential for an economy to thrive. Investing in healthcare institutions is another step for Ayala to improve the lives of Filipinos.
AC Health aims to build an inclusive healthcare ecosystem. It has built a roadmap to strengthen its commitment to the implementation of the UHC Law.
The company strengthens every pillar of its portfolio, from clinics, pharmacies, health technology, and hospitals, through process improvements, synergy, and further acquisitions.
Clinics:
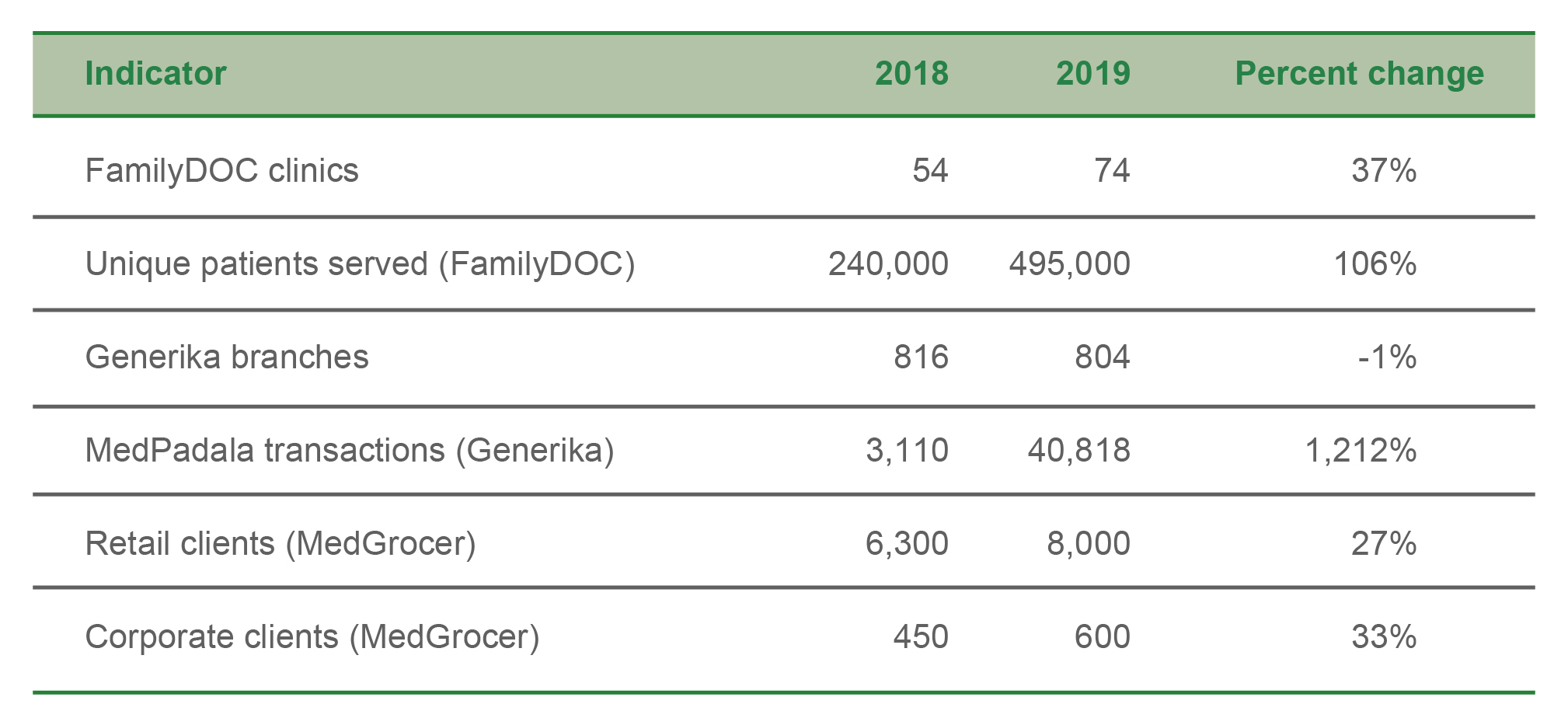
FamilyDOC expanded its network of clinics to 74 from 54 in 2018. The clinics served over 495,000 new unique patients. Turnaround time showed a nine-minute improvement from 45 minutes in 2018.
AC Health’s investment in Healthway added seven mall-based multi-specialty clinics and 40 corporate clinics to its network.
Pharma:
Generika’s 804 branches nationwide offer high quality and reasonably priced medicines. Its MEDPadala electronic gift checks ensure that money sent to loved ones is spent on needed medicines. MEDPadala transactions significantly increased to 40,818.
Investments in pharmaceutical products importer and distributor,
IE Medica and MedEthix, respectively, bring in a wider range of affordable medicines to AC Health’s Generika and FamilyDOC outlets accessible to low income communities.
Technology-enabled platforms:
MedGrocer, an online pharmacy platform, continues to provide a wide variety of affordable high-quality vaccines, medicines, and clinic supplies to its growing base of retail clients, which increased by 27 percent in 2019. It also grew its network of corporate clients from 450 covering 460,000 employees to 600 corporate clients covering about 520,000 individuals.
AIDE, AC Health’s home-based healthcare platform, continues to develop and provide a competent personal primary care option. It has nearly 800 medical specialists and healthcare professionals from over 70 cities and municipalities across the Philippines.
Hospital:
AC Health continues to expand its portfolio of medical facilities as it is poised to invest ₱2 billion to build the first cancer specialty hospital in the Philippines.
Partnerships:
Together with the Ateneo Professional Schools, AC Health organized the Health Leadership Summit that brought together key stakeholders from the government, private sector, and the academe to engage in meaningful discussion and collaboration towards the implementation of the UHC Law.
AC Health’s expansion of its healthcare facilities and investments increases its ability to reach more medically-underserved Filipinos.
ACCESS & INCLUSIVITY

AC Health
Target:
To champion Universal Health Coverage in the country by providing the largest primary care network, expanding access to quality and affordable medicines, and improving essential hospital and specialty services, touching the lives of one in five Filipinos
ACCESS & INCLUSIVITY

iPeople
Target:
To help ensure equal access for all women and men for 85 percent (1,258,095) of non-working population (aged 15 to 24) to affordable and quality secondary and tertiary education, including university, through our own schools and helping other institutions
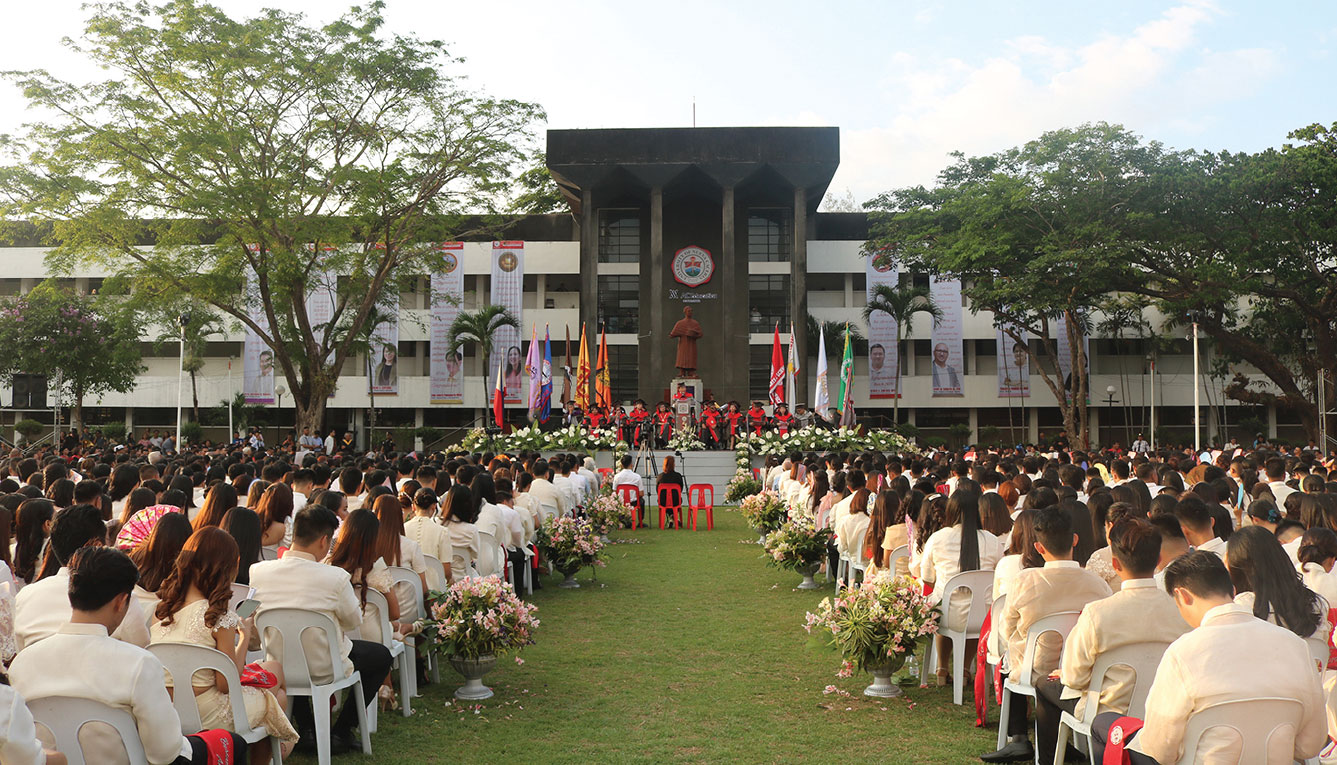

UNC successfully graduated college, high school, and elementary students.
Based on the 2017 Annual Poverty Indicators Survey (APIS)5, about three million Filipinos aged 16 to 24 years old were out-of-school children and youth.
Lack of access to quality education is one of the biggest barriers to Philippine development. At Ayala, we see this as a strategic area of work as it delivers multiple impacts in the development areas of poverty alleviation and human capital building, which we need for our businesses.
We believe addressing this challenge requires us to build scale by collaborating with other businesses, government, and communities, while optimizing available resources.
Since 2012, we have started investing in educational institutions and have been steadily growing our portfolio over the years. In May 2019, the Ayala and Yuchengco groups finalized the merger of AC Education and iPeople, placing seven educational institutions under one entity. These institutions can serve about 60,000 students, mostly within the 15 to 24 age range.
Our portfolio today covers primary, secondary, and tertiary educational formats.
Affordable Private Education Centers (APEC) Schools in Metro Manila, and in the provinces of Rizal, Cavite, Laguna, and Batangas
• Serves 15,815 junior and senior high school students for SY 2019-2020
– 44 percent are from the D and E market segments
– 5,225 students with government-subsidized scholarship
– 69 students with school-subsidized scholarship
• Successfully graduated 3,287 senior high school students
– Out of total graduates, 483 sought jobs and 93 percent were given job offers, wherein 71 percent accepted
University of Nueva Caceres (UNC) in Naga City, Camarines Sur
• Serves 7,617 students from elementary, high school and college for SY 2019-2020
– 57 percent are from the D and E market segments
– 4,242 students are with government-subsidized scholarship
– 55 students are with school-subsidized scholarships
• Successfully graduated 888 college students, 710 SHS graduates, and 89 elementary students
National Teachers College (NTC) in Manila
• Serves 10,632 students from high school and college for SY 2019-2020
– 67 percent are from the D and E market segments
– 8,957 students with government-subsidized scholarships
– 171 students with school-subsidized scholarships
• Successfully graduated 945 senior high school students and 1,159 college students
• NTC offers additional support for students to increase employability through the Professional Employment Program (PEP) program. In 2019, out of 177 PEP graduates who sought jobs, 159 gained employment within 90 days after graduation.
We have come a long way in building our capacity to meet the country’s growing need for access to quality education but we also know we still have a long way to go. We will continue to innovate better and look for more creative ways to tackle this challenge to bring our solution to scale.

Manila Water continues its efforts to deliver safe and reliable water.
Nearly seven out of 105 million Filipinos do not have access to potable water while more than 24 million do not have proper sanitation6.
Access to water and proper sanitation is a basic human right and fundamental to our development as a country. Ayala responded to the call of the government to improve the grossly inadequate water infrastructure when it entered the water and sanitation space in 1997. We considered it as an opportunity to contribute meaningfully to nation building.
With partners such as the International Finance Corporation (IFC), Manila Water was formed to focus on laying the water infrastructure throughout the Manila Concession East Zone. The goal was to continually address leakage and bring water pressure to a level that ensures round-the-clock water access to all residents in the area.
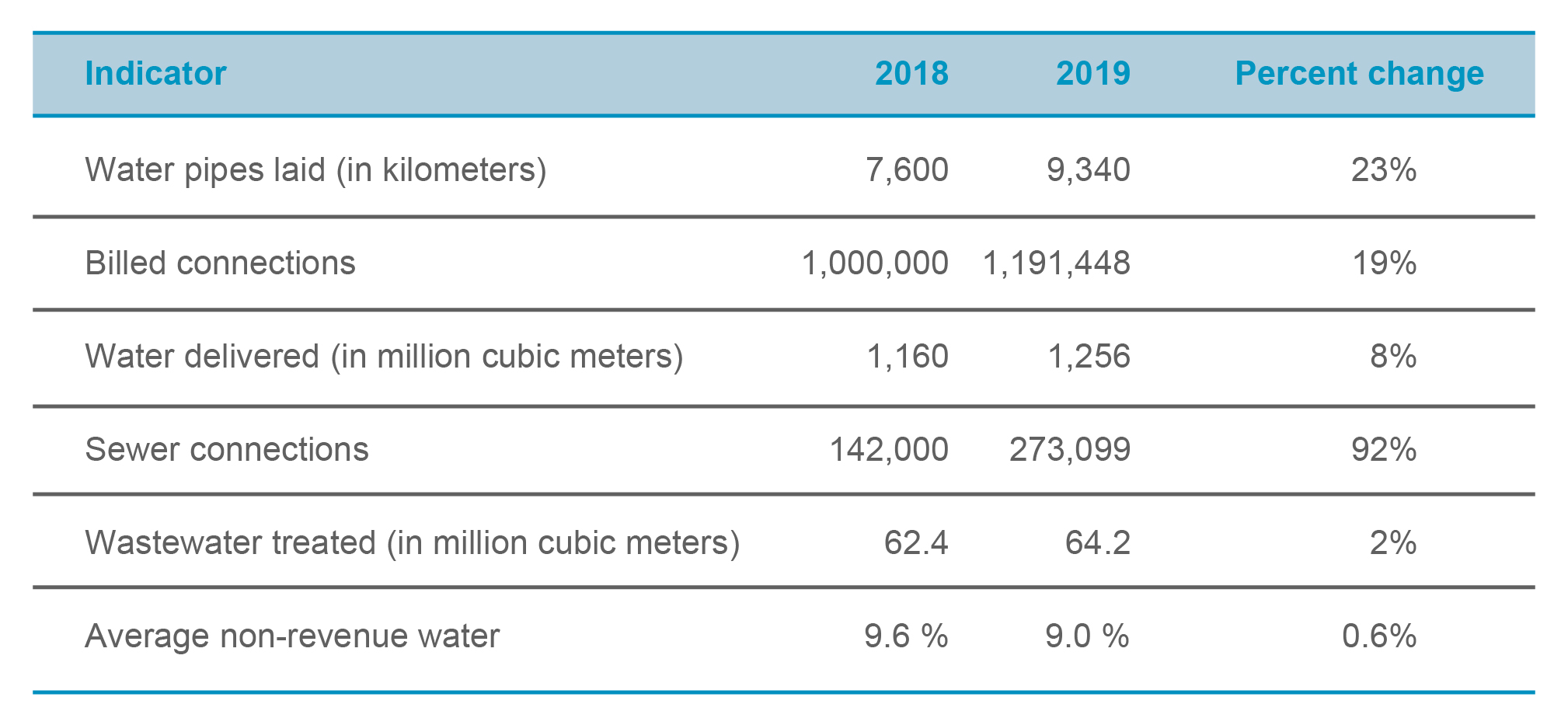
Over the years, Manila Water has invested over ₱166 billion to improve water and wastewater services. We have installed over 5,500 kilometers of pipes and built two new filter plants, 32 new reservoirs, and 113 pumping and booster stations.
These improved coverage in the Manila Concession from serving three million people in 1997 to over seven million people today. Among these are two million customers from the poor and marginalized sector, who now save up to 90 percent of what they would otherwise spend on vended water.
We have also rehabilitated and constructed 40 wastewater treatment facilities in the Manila Concession and five times more sewer network capacity to connect more residents to proper sanitation. In the Manila Concession, wastewater facilities treated 44.9 million cubic meters of wastewater and removed 6,302 tons of organic pollutants.
Despite recent challenges in water availability, Manila Water marginally increased water delivery compared to 2018. The completion of the Cardona Water Treatment Plant resulted in an additional 100 million liters of potable water per day.
Manila Water also reduced water losses to ensure that more water reached its customers. In 1997, water losses were at 63 percent in the Manila Concession. We managed to bring it down to 12 percent, saving 700 million liters per day. We further brought down the losses from 11.4 percent in 2018 to 10.4 percent in 2019.
Manila Water has since expanded its investment in local and international companies delivering water and wastewater services. Outside the Manila Concession, the company has presence in Bulacan, Boracay, Clark, Cebu, Laguna, Pangasinan, Tagum, and Zamboanga, as well as in neighboring countries such as Vietnam, Indonesia, and Thailand.
Enterprise-wide, Manila Water was also able to reduce water losses from 9.6 percent in 2018 to 9.0 percent in 2019. Across all business units, wastewater facilities were able to treat a total of 64.2 million cubic meters of wastewater and removed 13,440 tons of dissolved organic pollutants, helping preserve essential bodies of water.
Ensuring water access and availability and increasing sewerage coverage and capacity is a continuing work of Manila Water. We exert all efforts
to ensure that we fulfill this mandate and reach our SDG 6 target.
ACCESS & INCLUSIVITY

Manila Water Company
Target:
To provide equitable, reliable, and safe water access in all its concessions, and continuously increase access to new markets
Productivity & competitiveness

Ayala Corporation
Target:
To support full and productive employment and decent work for all and equal pay for work of equal value by ensuring employment remuneration is 10 to 20 percent above the industry average
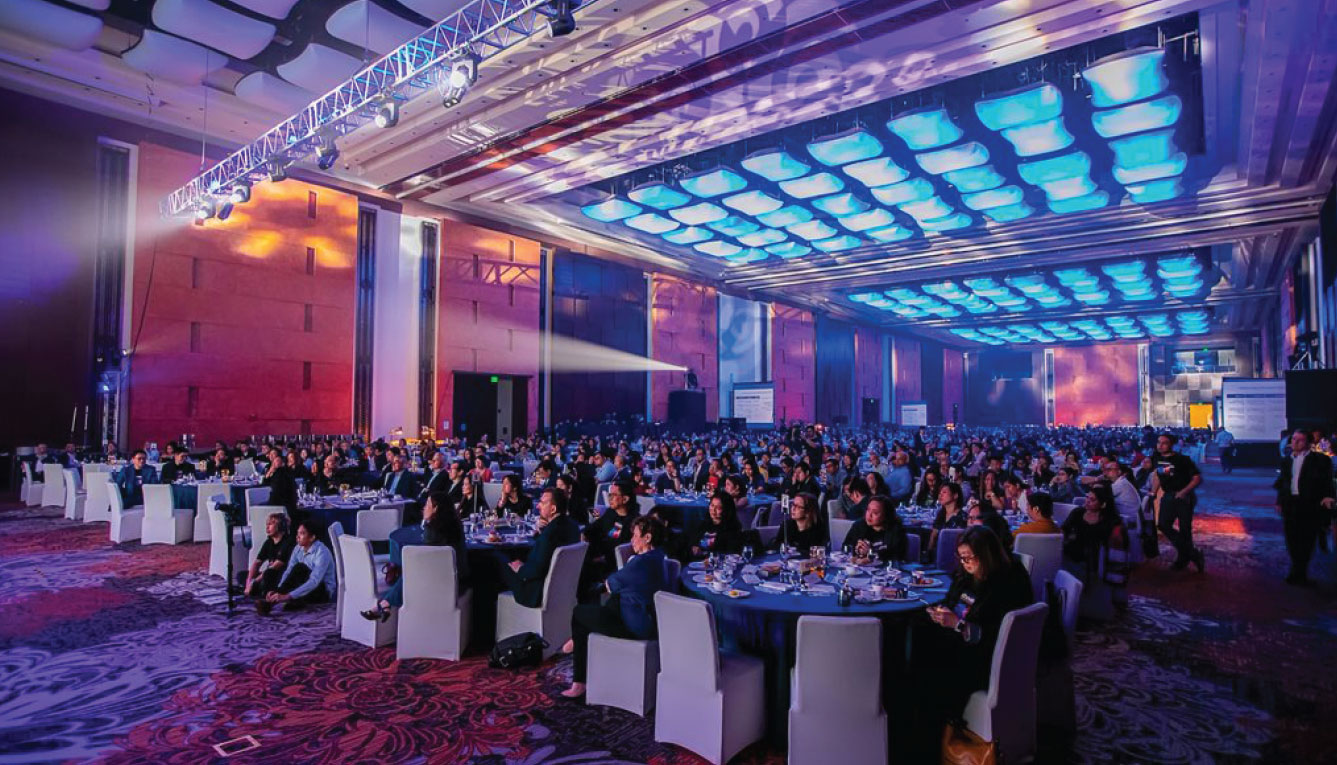

Ayala annually conducts summits for its workforce.

According to the Philippine Statistics Authority, the national employment rate in 2019 is estimated at 94.6 percent. However, 13.9 percent of these are underemployed, and expressed interest in more job opportunities.
As one of the biggest business houses in the country, Ayala recognizes
its responsibility to help address this gap.
Ayala creates a workplace that ensures all its 72,000 employees achieve their full potential, recognizing that its continued growth is propelled by productive and engaged employees.
Our business units employ a consultative process in defining career development paths. Training needs are jointly determined by employees and their managers. On the average, every Ayala employee received 60 hours of training in 2019, with those in rank-and-file positions given the most at an average of 101 hours of training.
We strive to provide a good employee experience from the moment one gets hired in any of our companies. Best practices we noted include flexible working hours, teleworking with the use of technology, work hubs in strategic locations to reduce employee commute, and provision of digital tools to improve productivity. We also drive productivity by streamlining processes, providing appropriate authority, and removing obstacles that get in the way with job efficiency.
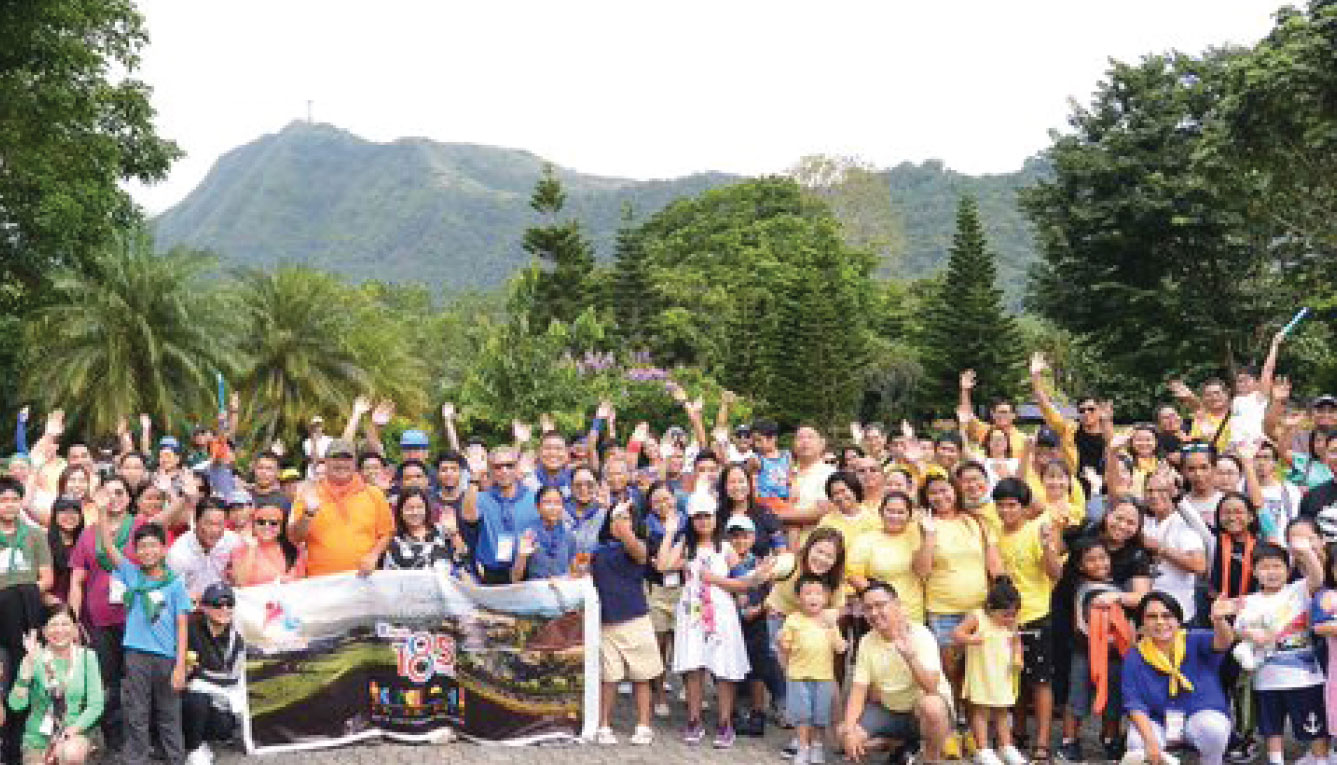

Ayala provides leisure activities to promote work-life balance.
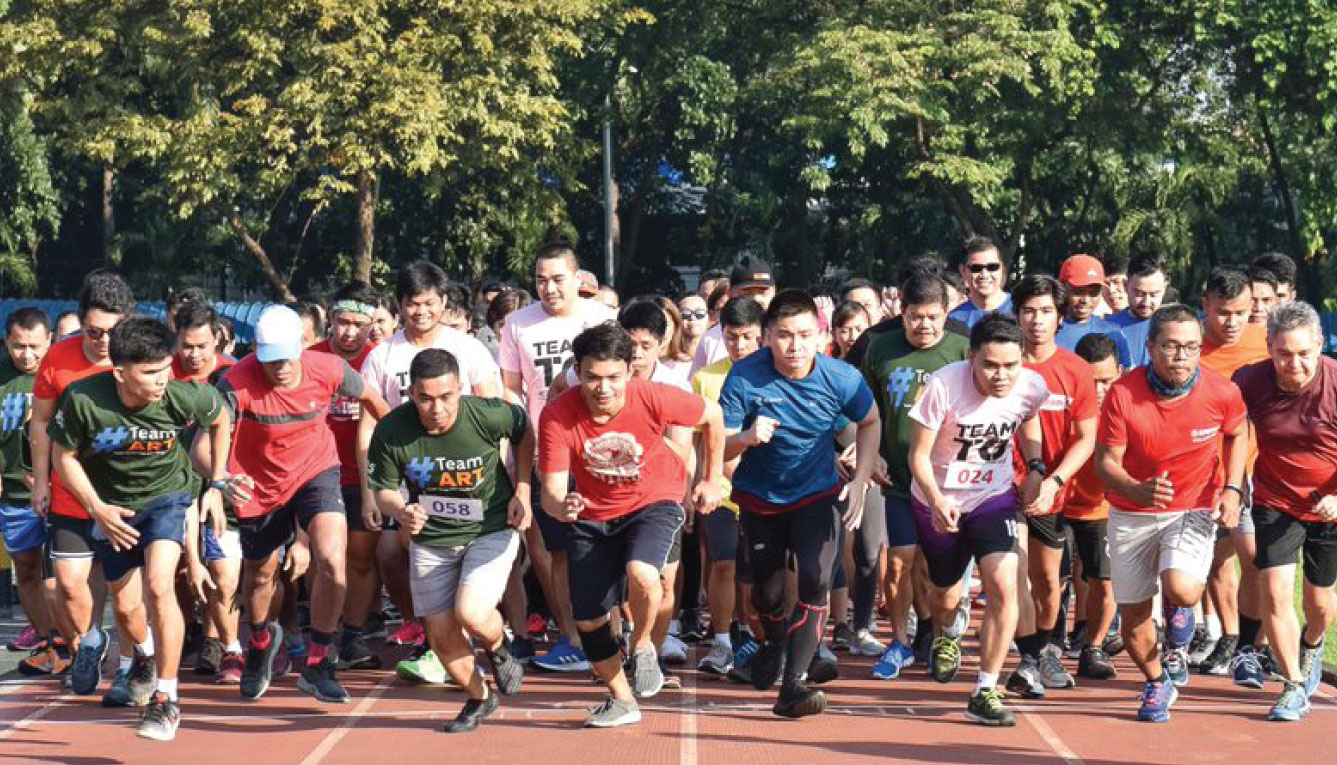

Ayala annually conducts sports events for its employees.
We encourage diversity, respect, and healthy exchange of ideas to foster good working relationships among our employees. Non-discrimination in the hiring, training, promotion, and other processes is strictly observed. Gender diversity among permanent employees is at a 1:1.33 men-to-women ratio.
Our benefit packages remain competitive. We offer benefits beyond regulatory requirements such as health coverage and stock options. Results of a 2019 survey show that Ayala Corporation’s employee compensation is about 10 percent above industry average.
Keeping our employees productive and engaged is a continual improvement process. We keep up with emerging workplace best practices and the evolving expectations of our people, especially the younger professionals. We continue to deliver meaningful and productive jobs for our employees and provide career growth opportunities to help close the underemployment gap of the country.
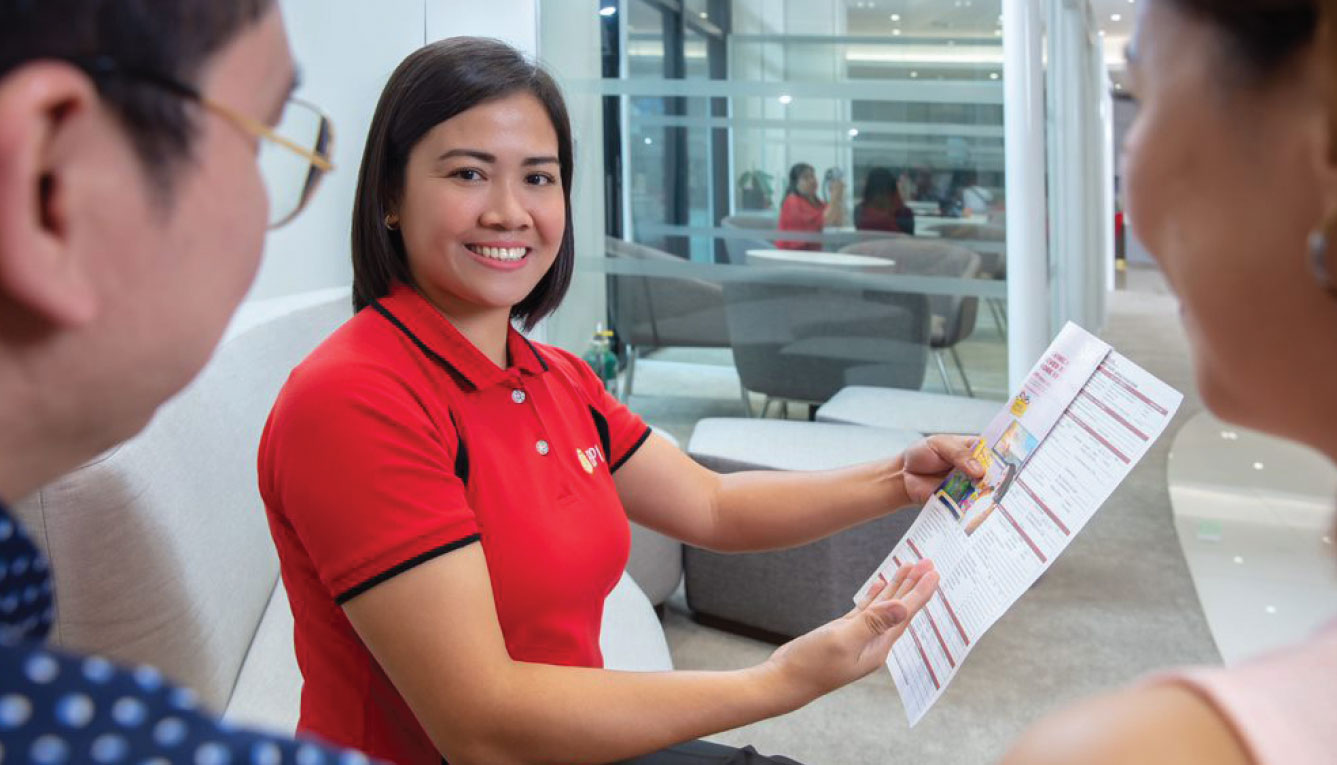

BPI reaches more Filipinos through its array of products and services.
According to the latest financial inclusion survey by the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas, over 70 percent of Filipinos do not have access to formal financial services. This curtails their ability to improve productivity and quality of life.
Ayala tackles this challenge through its subsidiary, BPI, which considers this gap as an opportunity to grow its market and contribute to poverty alleviation and human development. Its financial services drive entrepreneurial activity, productivity, and overall economic growth.
BPI reaches more Filipinos and businesses by expanding its deposit franchise and delivery infrastructure in Metro Manila and in key cities. This expansion is balanced and complemented by outlays in its digital infrastructure.
To cater to the underbanked market’s needs for credit facilities access,
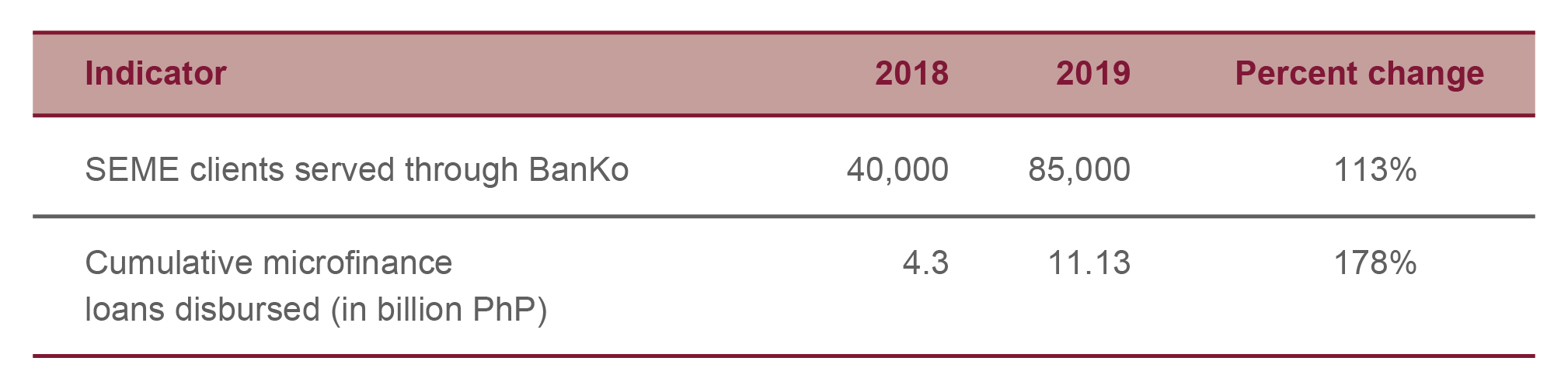
BPI repositioned its microfinance business strategy under BPI Direct BanKo, Inc. from a mobile-based to a more traditional in-person model, targeting self-employed micro-entrepreneurs.
BanKo grants business loans based on well-grounded credit parameters and provides quick turnaround times and lower interest rates versus traditional money lenders. The shift to a more traditional business model allows for a more effective know-your-customer process, leading to efficient collection and reduction in non-performing loans. Its 300 branches nationwide serve a total of 100,000 self-employed micro-entrepreneurs (SEME) with the help of 800 loan specialists hired in 2018.
Through these innovations, BPI has more than doubled the number of SEME clients served, and almost tripled its disbursed microfinance loans from 2018 to 2019.
These recent years have been very encouraging for BPI as its financial inclusion strategies have been proven effective. It looks to scale these even further in the next few years to meet its commitment to reach at least 25 percent of the underbanked population by 2030.
Productivity & competitiveness

BPI
Target:
To expand access to banking and financial services to 25 percent of the underbanked population of the Philippines (addressable C and D markets)
Productivity & competitiveness

Globe Telecom
Target:
To lead the country’s digital transformation by significantly increasing access to information and communications technology for consumers and businesses, providing universal and affordable internet access in the Philippines for 90 percent of the population
Globe continues to innovate digital products for Filipinos.
A total of 76 million Filipinos have access to the internet. A good 72 million of them connect to the net via a mobile device7.
This presents a great opportunity for Ayala as it democratizes access to innovative digital products and services. Thus, making healthcare, education, financial services, including mobile payments, insurance, and credit, available to every Filipino.
Ayala’s digital transformation work is primarily carried out by its subsidiary, Globe, which actively invests in expanding its nationwide network. Beginning in 2011, Globe’s US$ 700 million seven-year network modernization program drove adoption of pioneering technologies and innovation in products and services, such as digital lifestyle play, content partnership with iconic global brands, and deployment of early-stage 5G network connectivity.
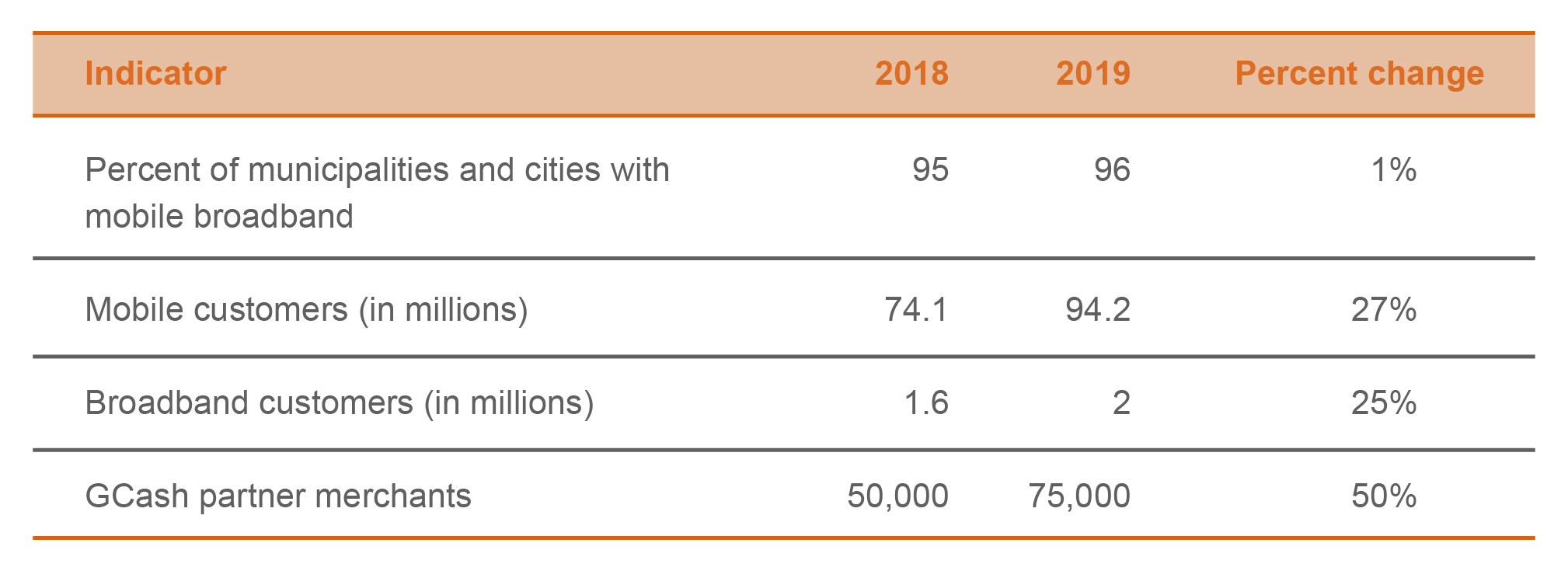
In 2019, Globe increased deployment of cell sites by 139 percent and increased base stations by 69 percent compared to 2018. This contributed to an increase in mobile customers to 94.2 million from 74.1 million in 2018. Globe also maintains two million broadband customers.
The company revolutionizes access to financial services through Mynt, with two platforms—Fuse Lending, a fintech-enabled lending institution, and GCash, a mobile wallet app for financial services.
GCash now has over 20 million customers and over 75,000 participating merchants, a 50 percent increase from 2018. GCash also maintains more than 30,000 cash in and cash out outlets to serve its customers. Mynt has partnered with local government units (LGUs) to offer GCash as an alternative mode of payment (Makati and Quezon City LGUs) and payroll allowance disbursements (Makati, Manila, Boracay, Siargao, and Semirara LGUs).
Operating in a highly competitive and fast-paced industry, Globe continues to evolve and expand its network and services with a clear focus on achieving its target to reach more than 90 percent of the country’s 1,101 cities and municipalities.
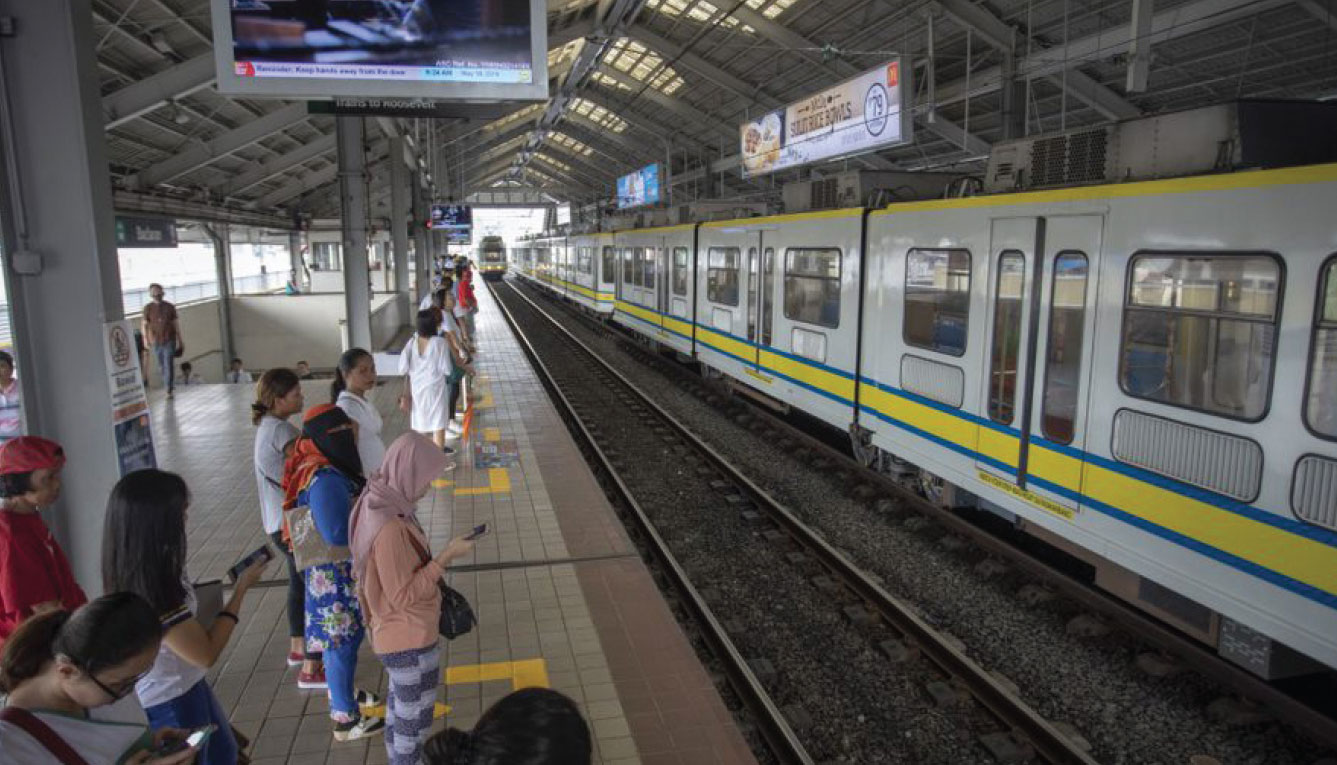

AC Infra strives to improve urban mobility, logistics, and mass transport.
Rapid urbanization and lack of infrastructure have led to significant challenges in the transport and logistics sector of the Philippines. These challenges require massive investments and development towards mass transportation and urban mobility.
Good transport and logistics infrastructure facilitate steady and seamless flow of people, goods, and services—all of which are essential for a more productive economy.
AC Infra invests in strategic projects to meet the growing infrastructure needs in areas of mass transportation, logistics, and urban mobility primarily through public-private partnerships.
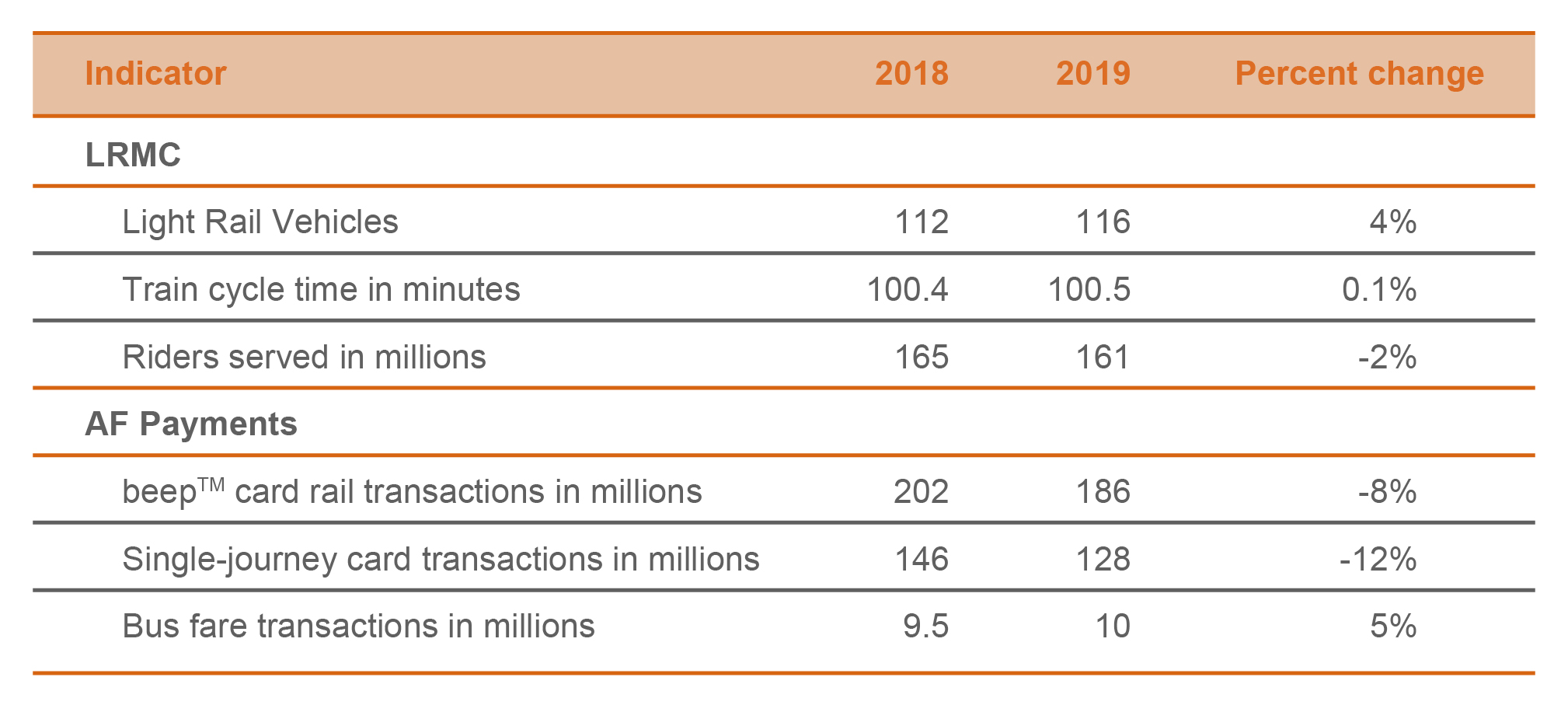
LRMC, AC Infra’s rail service company, increased its fleet for LRT1 and maintained its train punctuality rate despite the longer cycle time (the time it takes for a train to complete a journey from a terminal station and back). LRMC’s average daily trips remain to be stable.
AF Payments offers a contactless payment platform called beepTM which can be used for rail, bus, retail, and tollway transactions. The total number of beepTM and single journey rail transactions decreased due to the closure of the Cubao to Santolan segment of LRT2. AF Payments facilitated more transactions for point-to-point (P2P) bus routes, retail, as well as tollway transactions.
AC Infra is steadfast in meeting the infrastructure needs of the country in a more efficient way. The company is also designing a mechanism to account for greenhouse gas emissions avoided in its low-carbon processes and activities.
Productivity & competitiveness

AC Infrastructure
Target:
To upgrade infrastructure to make them sustainable, with increased resource efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes with 36,135 tons CO2 equivalent avoided
Productivity & competitiveness

Ayala Land
Target:
To enhance inclusive and sustainable urbanization by increasing sevenfold the number of launched affordable housing units
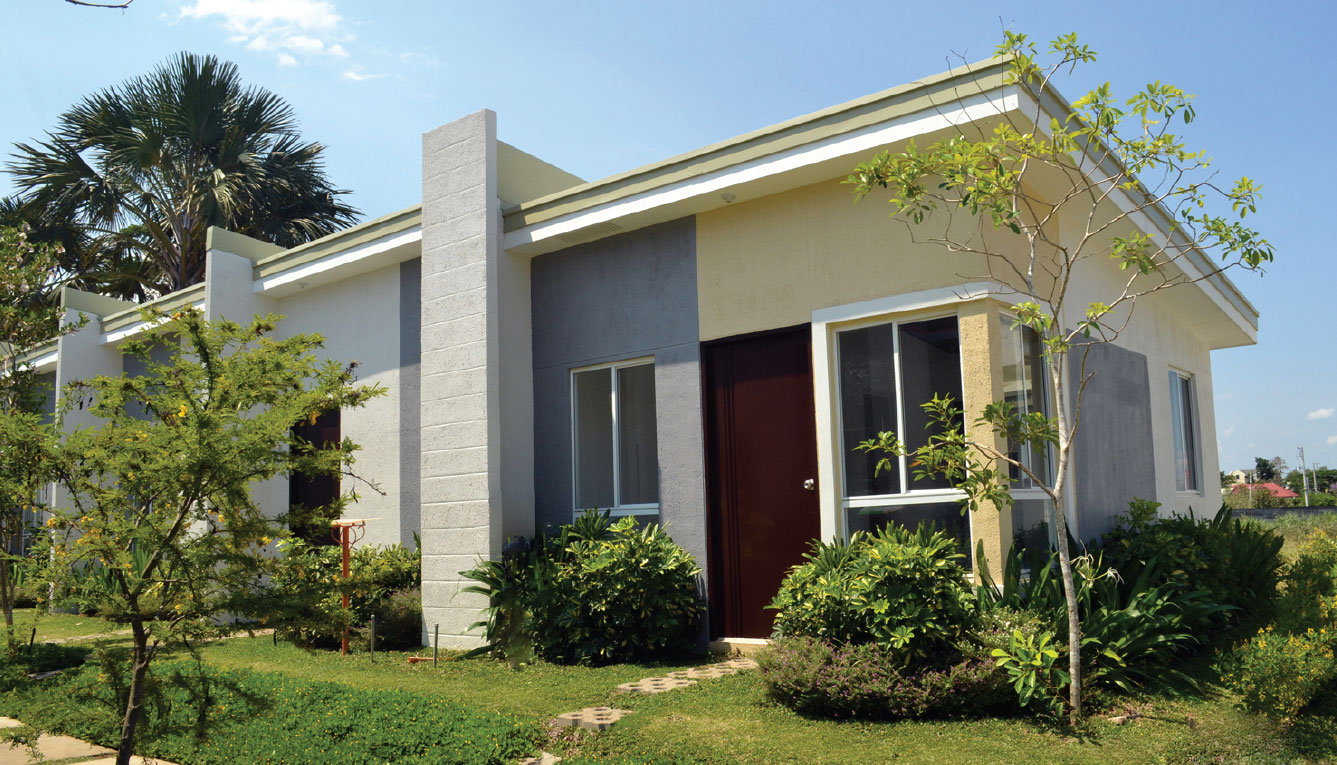

Ayala Land builds reasonably-priced residential units.
The Philippine Statistics Authority reported that construction activity increased by 10.4 percent in the first quarter of 2019 compared to the same period last year. By type of construction, residential buildings accounted for 69.2 percent of the total. However, figures for housing projects for the lower economic groups could do better by considering the country’s housing needs, which is projected to reach 6.5 million by 2022.
Affordable housing provides vulnerable populations with economic security and stability. Ayala recognizes its strategic position to create resilient and inclusive communities through its property development arm, Ayala Land.
Ayala Land looks to scale its development of properties and estates across the country while maintaining its approach of integrating sustainability with economic development and social welfare.
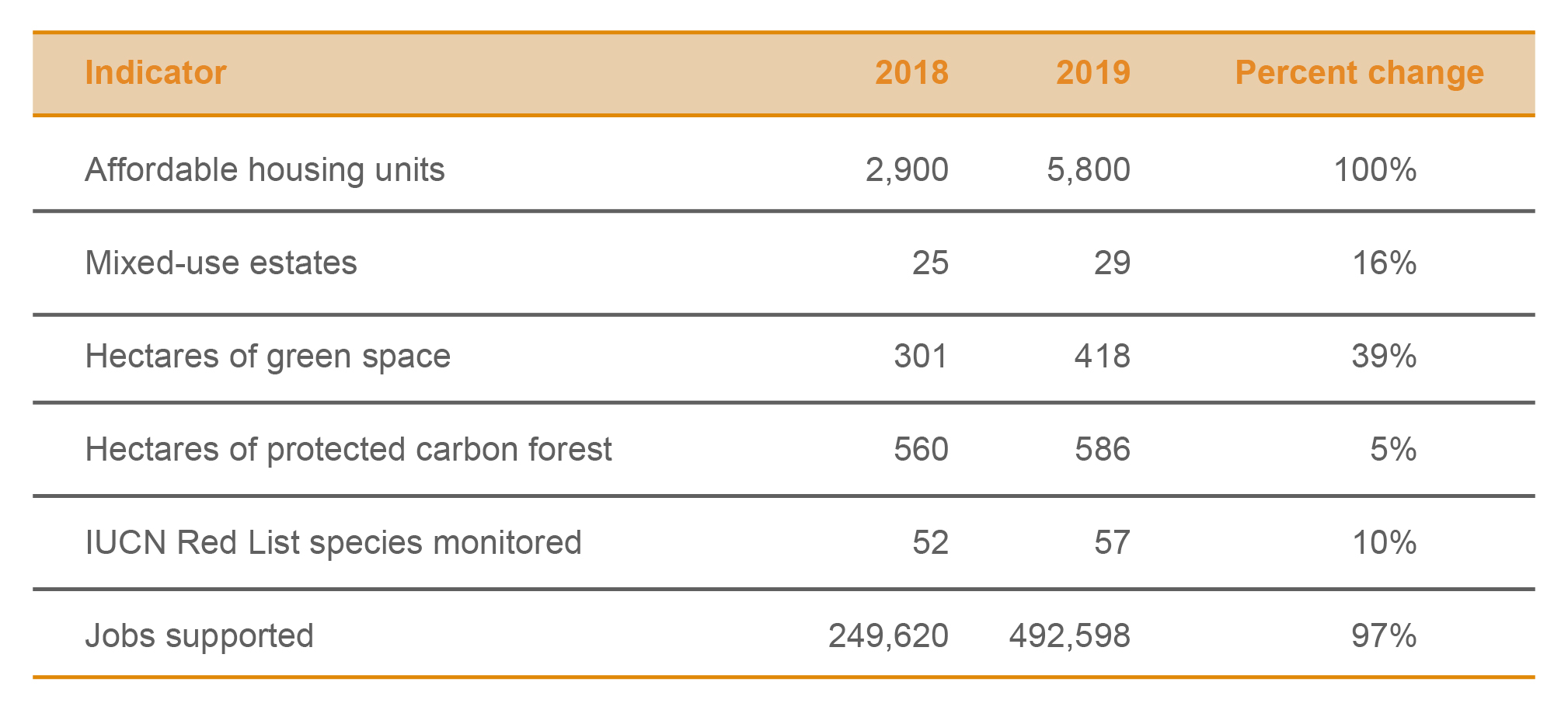
Ayala Land contributes to filling the gap for value-for-money residential units by driving building design innovation to bring down the unit cost without compromising quality and sustainability. In 2019, it doubled its affordable units to 5,800 from 2,900 in 2018.
Ayala Land contributes to sustainable urbanization by ensuring all its developments meet the specifications under these four focus areas. This framework serves as a general guide to property development and operations to mitigate sustainability risks and provide value to the business, environment, and society.
• Site Resilience. We strengthen our sites to quickly recover from environmental stress by undertaking technical due diligence to screen for geohazards, providing space for refuge and rainwater absorption, and using native plants and trees for landscaping.
• Pedestrian and Public Transit Connectivity. We adhere to principles that guide our masterplans to provide alternatives to car use in our estates. We aim to provide more opportunities for walking and commuting by providing pedestrian-only areas and walkways, transit stops and terminals in estates and malls, and ensuring connectivity during construction and operations.
• Eco-Efficiency. We use our resources judiciously and commit to reduce our GHG emissions by implementing energy and water conservation programs, waste management programs, and by committing to be carbon neutral by 2022.
• Local Economic Development. We build large-scale, integrated mixed-use sustainable estates across the country. We prioritize local hiring and give opportunities for homegrown businesses.
To date, Ayala Land has 29 mixed-use estates and an aggregate size of 9,935 hectares. In these estates, Ayala Land is able to co-create sustainable communities by providing Filipinos with better quality of life while spurring new centers of growth.
Ayala Land has deliberately planned and allocated a total of 418 hectares of green space, hosting close to 70,000 native trees and 57 species of IUCN Red List species. It is also protecting 586 hectares of carbon forest that stores 80,000 tonnes of CO2e. Ayala Land achieved a 72 percent reduction in commercial properties’ net GHG emissions in 2019. The entire operation of Ayala Land, including its tenants, merchants, and suppliers supports an estimated 492,000 jobs.
Ayala Land continues its work to deliver its commitment of enhancing inclusive and sustainable urbanization, staying on track with its target number of reasonably-priced residential units built by 2030.
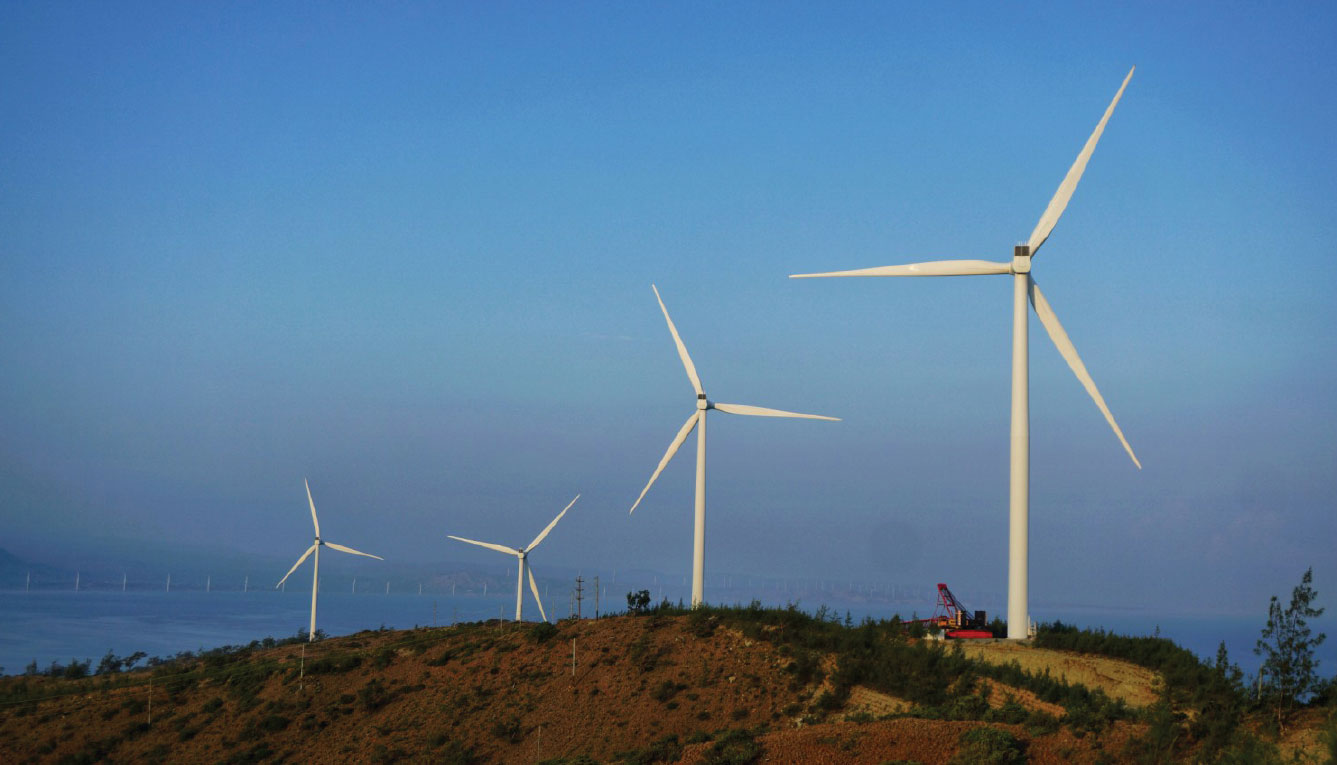

AC Energy continues to increase its renewable energy portfolio.
To fuel its rapid economic development, the Southeast Asian region is expected to increase its energy demand by 60 percent in the next 20 years, with coal being the primary power source. The improvements on cost efficiency and policy support towards renewable energy has increased the viability of renewable energy projects in the region.
With the increasing clamor for a low-carbon future, Ayala sees a significant opportunity to lead the region in the development of renewable energy through its energy platform, AC Energy.
Achieving a low carbon portfolio is at the core of AC Energy’s business strategy and serves as one of the pillars of its Environmental and Social Policy, which embodies the company’s commitment to sustainability and social responsibility.
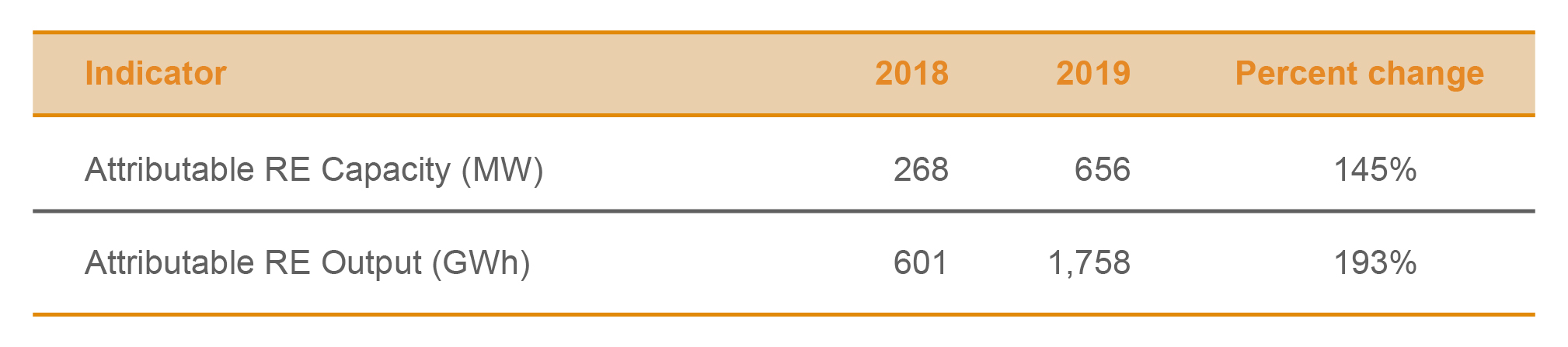
AC Energy is scaling up its renewable energy (RE) portfolio by investing in key markets in the Philippines, Indonesia, Vietnam, Australia, and India. In 2019, the company more than doubled its 2018 attributable RE capacity in its portfolio.
Locally, AC Energy’s acquisition of PHINMA Energy in 2019 expanded its capabilities to build and operate power projects while balancing its renewable and thermal portfolios.
The company also increased its attributable energy output to 3,500 GWh, 50 percent of which came from renewable energy sources.
AC Energy’s rapid growth in renewables in 2019 builds up the company’s momentum towards its target: a renewable energy portfolio of 5 GW by 2025.
responsible, growth & innovation

AC Energy
Target:
To increase its renewable energy portfolio to 5 GW in the Philippines and in foreign markets
responsible, growth & innovation

AC Industrials
Target:
To enable the first Philippine-manufactured, commercially viable, and market-accepted electric vehicle, resulting in reduced emissions. For AC Automotive to promote low emission vehicles, ensuring that each brand offers a minimum of one model not fully dependent on a combustion engine powertrain. Globally and on the manufacturing side, for IMI to promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization by demonstrating manufacturing value add of USD1 billion across all developing countries where it has operations
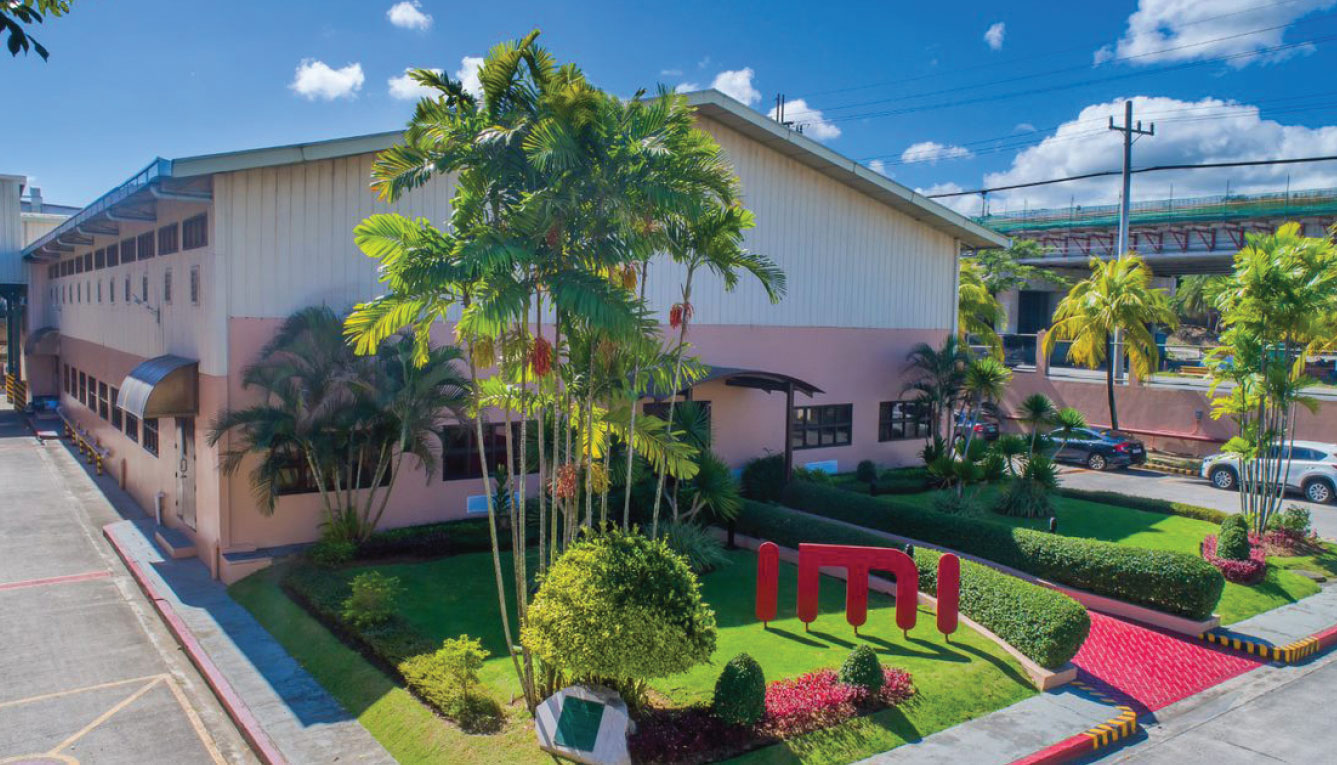

AC Industrials maximizes technology innovation through its EMS company, IMI, and its auto dealership network, AC Motors.

The Philippine government has been promoting the use of electric vehicles across the country, including as a form of public transportation. Executive Order 488 reduced the tariff rate for e-vehicle components to zero, encouraging e-vehicle manufacturers to import components.
With the shifting global landscape towards innovative and sustainable mobility-based technologies, Ayala seeks to participate in the manufacturing space through its subsidiary, AC Industrials.
AC Industrials optimizes opportunities offered by new technologies through investments in companies with strong industrial technology capabilities.
Integrated Micro-electronics Inc (IMI), its EMS manufacturing arm, delivers emerging technologies for automotive, smart energy, and connectivity solutions in 22 plants across the globe. Its manufacturing value reached US$419 million in 2019, a five percent decrease from 2018.
AC Motors, its automotive dealership arm, is exploring possibilities to bring in more eco-efficient automotive models without compromising passenger safety and driver comfort and convenience.
AC Industrials is gradually building its capacity to enable local adoption of electric vehicles leveraging IMI’s strong manufacturing capabilities and AC Motors’ extensive automotive network.
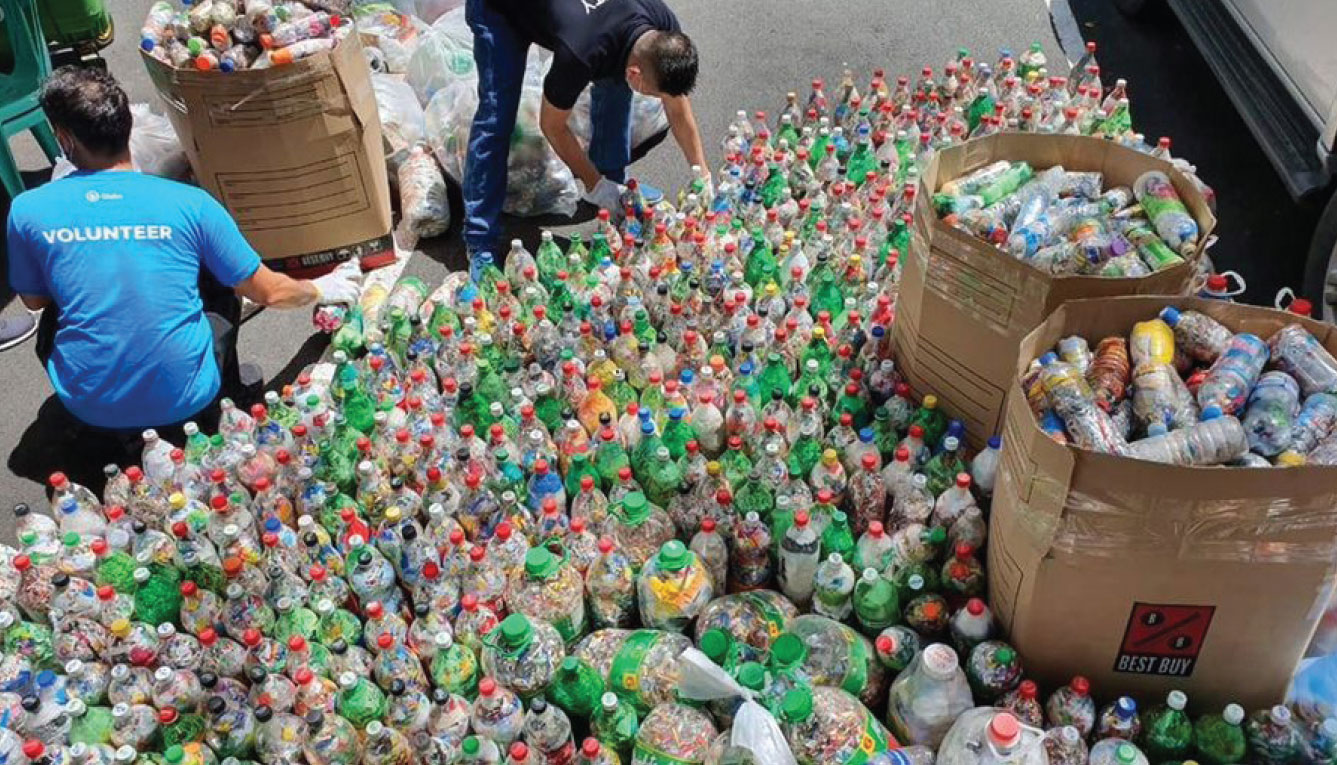

Ayala ramped up efforts on waste management.
A Report published in 2012 on the Philippine Ecological Footprint claimed that the rate of consumption of resources was more than twice the capacity of its domestic ecosystem to generate. This overconsumption is not sustainable and compromises the ability of future generations to meet their needs.
Ayala recognizes that with the scale of its business and the increasing demand for its products and services, its consumption of renewable and non-renewable resources is quite significant. Every year, Ayala diligently tracks its materials consumption and continually innovates to improve its materials efficiency.
In 2019, our materials intensity slightly improved from 2.66 to 2.64, showing that less materials were used per unit of business output. Our biggest consumption of materials is in Ayala Land’s construction activities. To support materials circularity, Ayala Land purchases materials with recycled content. It also designs properties that optimize the use of materials without compromising structural integrity and quality.
As part of its commitment to SDG 12, Ayala is currently conducting a study for a group-wide waste management strategy in line with its target to substantially reduce waste generation through reduction, recycling, and reuse. The goal is to develop practices and design processes that systematically reduce solid waste that reaches local landfills and the oceans.
In 2019, Ayala generated 48,632 tonnes of non-hazardous waste (such as recyclables, residuals, and food and compostables), a decrease of about 11 percent from the previous year, despite growth in our operations. Food waste accounts for 30 percent of our total generation. In 2019, by opting for composting, we diverted 15 thousand kilograms of food waste from landfills. We are currently improving our food waste collection to divert most, if not all into composting and other uses. Non-biodegradables account for 70 percent of our total waste generation. About 35 percent or 11,794 tonnes of that were sent to recycling.
We recognize the difficulty of reducing absolute materials consumption in our context as a developing country. However, we strive to become more efficient in the way we use them. We also do what we can to recover waste for recycling and make procurement choices that drive growth of our circular economy.
responsible, growth & innovation

Ayala Corporation
Target:
To achieve an ambitious material footprint that demonstrates sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources
responsible, growth & innovation

Ayala Corporation
Target:
To achieve an ambitious material footprint that demonstrates sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources
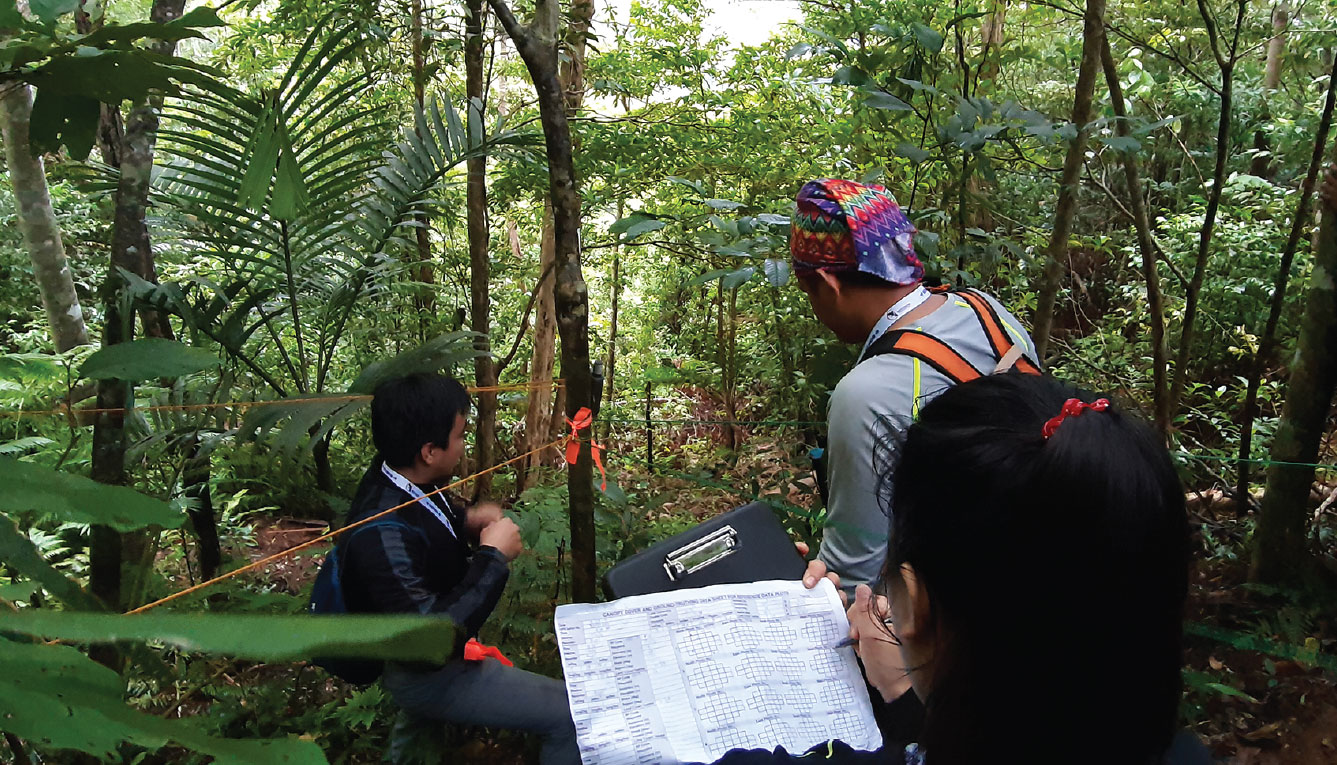

Canopy cover measurement for forest carbon calculation.
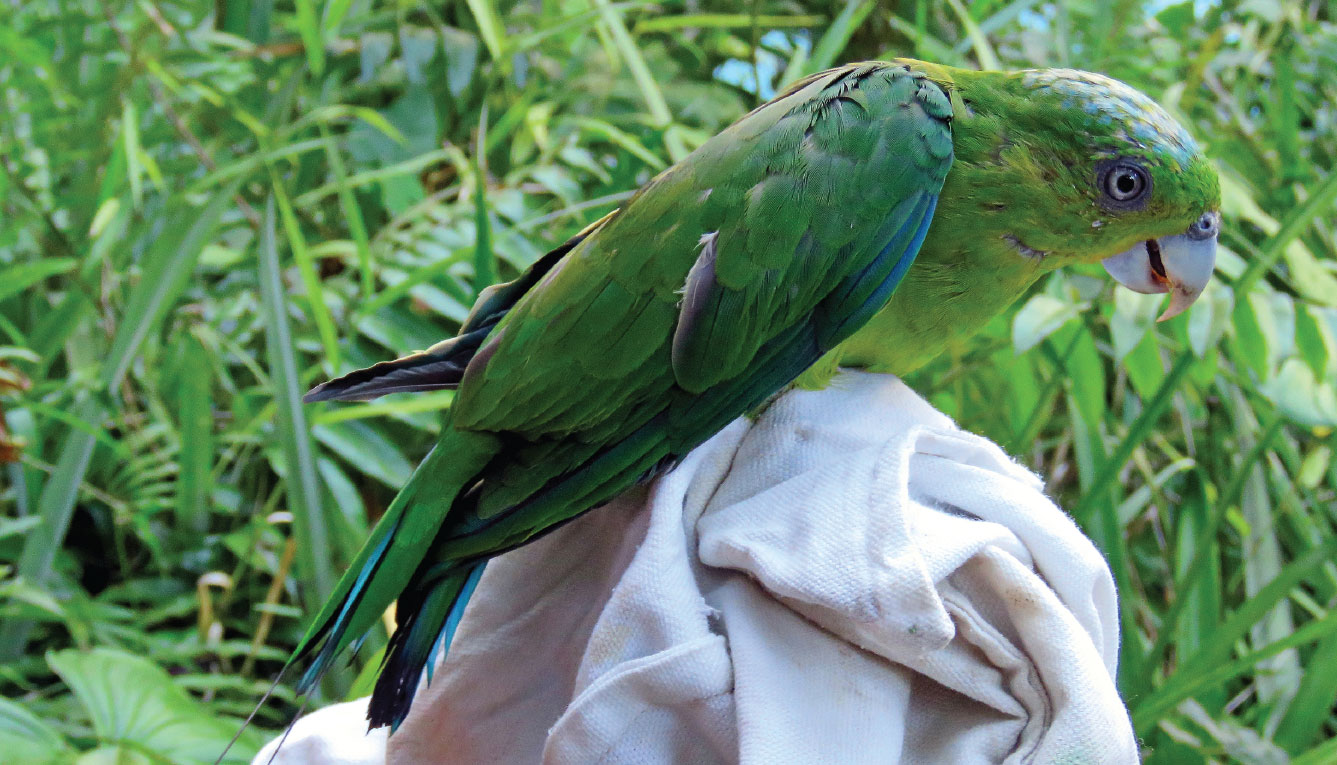

The Mindoro Racquet-tail (Prioniturus mindorensis*) is tagged as vulnerable by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
Based on UNEP’s 2019 Emissions Gap Report, global emissions are on track to reach 56 Gt CO2e by 2030, more than twice the prescribed levels.
To respond to the growing urgency for climate action, Ayala has refined its approach to tackle climate change across three fronts: mitigation, adaptation, and innovation. This group-wide strategy embodies Ayala’s commitment towards addressing climate as a sustainability issue and promoting climate action under SDG 13. It continues to monitor its GHG emissions across the group, and implements mitigating measures through its business units.
At the boardroom, Ayala is studying the financial implications of climate-related risks as part of its risk management process.
Ayala will structure its climate action and investments based on results of data analysis showing how different climate scenarios can affect its businesses on physical, regulatory, market, and other levels.
On the ground, Ayala is building climate resilience by managing carbon forests, protecting watersheds in its business areas, and initiating reforestation activities across the Philippines.
Its flagship program, Project Kasibulan demonstrates how business can work with communities to create a sustainable and mutually beneficial forestry project.
Project Kasibulan
The Ayala Sustainability Council embarked on an initiative to conserve the environment through reforestation. Project Kasibulan, which in Filipino stands for growth and nurture, is now on its third year and has expanded its scope and
objectives beyond reforestation efforts.
The development of the community-based Mindoro Forest and Biodiversity Program is Project Kasibulan’s most significant achievement for 2019. The program completed its carbon forest baseline inventory and economic and sociological assessments of several municipalities. Results from these studies will be instrumental in integrating livelihood with climate adaptation and in promoting green jobs and ecopreneurship among local communities. It is part of Ayala’s commitment of nurturing ecosystems and communities to create a sustainable and climate-resilient Mindoro.
Volunteers rising
This project is sustained yearly through the efforts of Ayala citizens in the spirit of volunteerism. Project Kasibulan volunteers have clocked in around 5,000 volunteer hours from Ayala employees whose involvement in the project serves as an impetus for more sustainable lifestyle choices. This year saw cohorts of volunteers taking part in the reforestation efforts of two sites: Ipo Dam in Norzagaray, Bulacan, and North Luzon Renewables in Pagudpud, Ilocos Norte.
• Project Kasibulan at Ipo Dam in Norzagaray, Bulacan
– 46 volunteers from across the Ayala group helped reforest the Ipo Dam watershed
– 1,552 volunteer hours
– 1,000 seedlings planted over two hectares of land across the watershed
• Project Kasibulan at North Luzon Renewables in Pagudpud, Ilocos Norte
– 61 volunteers from the Ayala Group Internal Auditor’s Network helped reforest a section within the 625 hectare forest land occupied by the wind farm
– 3,406 volunteer hours
– 1,210 seedlings planted
Addressing climate change and its risks to our businesses will remain an important priority of the group. Ayala leverages its diversified portfolio to drive significant impact in supporting our transition to a resilient and low-carbon economy. Our real estate arm, Ayala Land, champions the work on building low-carbon and resilient communities. Our energy arm, AC Energy, actively supports the transition to low carbon energy. Our bank, BPI, leans towards financing low carbon and resilient investments. The environmental commitment and initiatives of Ayala is bringing it closer to delivering its targets under SDG 13.
Ayala believes that sustainability is key to bridging critical environmental, social, economic, and governance gaps that have disadvantaged many Filipinos.
In 2012, we crafted a sustainability philosophy, which articulates our thinking around responsible and inclusive growth and its relevance to our Business. We then developed the Ayala 360o Sustainability Reporting Framework to better
ground this thinking into our business and clarify how we measure our performance.
When the UN SDGs were formally launched in 2015, we were ready to align our transformed business ambitions to these long-term goals. We then decided to be more strategic and focused in our approach through our Ayala Sustainability Blueprint. The updates provided show where we are in these targets.
We have made notable gains in bridging the Filipino to 2030, but as shown in this year’s performance, there is much to be done. We will be more deliberate in monitoring and evaluating our progress, making changes whenever necessary,
and allocating resources more appropriately, so that our businesses truly create shared value.
3 Philippine Statistics Authority, 2018
4 Philippine Statistics Authority, 2018
5 Philippine Statistics Authority, 2018
6 According to water.org, a global non-profit organization that conducted research, designed, and ran pilot projects for water and sanitation in the Philippines.
7 According to Digital 2019, a report from Hootsuite and We are Social at www.datareportal.com.





