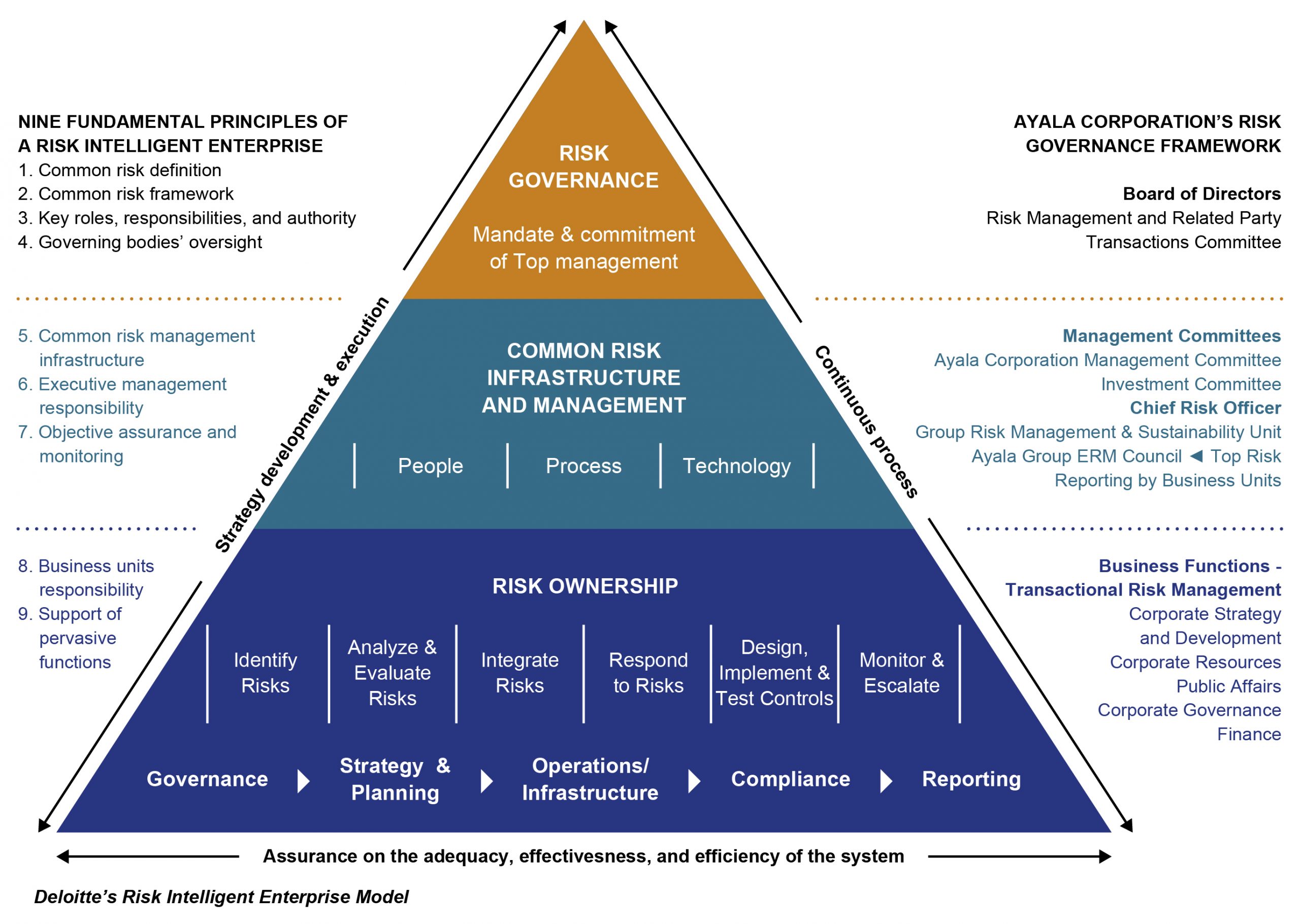
Designed to inspire integrated thinking, Ayala’s risk management framework is based on Deloitte’s concept of the Risk Intelligent Enterprise, which integrates nine principles related to responsibilities of the board, senior management, and business unit leaders. This framework supports the broader principles of ISO 31000 risk management standard, such as integration, structured and comprehensive, inclusive, and human and culture factors.
At the apex of the risk intelligent enterprise is risk governance—the unifying touchstone and guide to the organization’s risk management efforts. It seeks not to discourage appropriate risk-taking, but to embed relevant and effective risk management procedures into all of an enterprise’s business pursuits.
By treating risk as intrinsic to the conduct of business, risk intelligent governance elevates risk management from an exercise in risk avoidance to an essential consideration in every decision, activity, and initiative.
Risk Governance
Oversight for the operationalization of the Ayala’s risk management framework is entrusted to the Board of Directors through the Risk Management and Related Party Transactions Committee, which provides transparency and visibility into the corporate and the group’s risk management practices.
The Chief Risk Officer (CRO), being Ayala’s risk management advocate, reports to the Committee any improvement in the design, implementation, and maintenance of the enterprise risk management roadmap. The Group Risk Management and Sustainability Unit supports the CRO by conducting activities that will enhance the risk-aware culture and improve the risk management program in the organization. It also convenes the Ayala Group Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Council, composed of risk officers of Ayala business units, as a platform for sharing best practices on risk management. Business unit leaders are risk owners who are responsible for managing the risks they face in the day-to-day operations within the established risk governance framework. The Internal Audit Unit assesses the effectiveness of the risk mitigation measures proposed by the risk owners and provides an independent assurance of the adequacy, effectiveness, and efficiency of the risk management process.
Risk Infrastructure and Management Strategy
Ayala has a seven-year roadmap that communicates its journey of embedding a robust risk management process in support of achieving its business objectives and becoming a resilient organization. Several programs at the corporate and group-wide level were undertaken over the period of six years (2013 to 2019). These programs cover people, process, and technology.
People
In Ayala, risk is everybody’s business. We continuously equip our risk owners and their team members with ways how to identify, assess, evaluate, and manage risks that they face in their daily operations. We also conduct a risk culture survey every three years (2015 and 2018) to check if we are on track in strengthening the risk-aware culture in the organization.
Process
Ayala’s risk management practices transcend mere compliance. The shift was driven by the mindset that understands the interconnectedness and interdependency of risks that require collaborative risk mitigation strategies. Silos were broken down through risk assessment methodologies, such as the black swan approach, risk interaction mapping, bow-tie analysis, and risk sensing.
From 2016 onwards, Ayala intensified its risk management program by capitalizing on activities that linked risk management with business strategy, further strengthening the practice at all levels of the organization. In 2018, Ayala focused on the value proposition of risk management by assessing the effectiveness of its risk management program and streamlining opportunities for positive impact. This started the conversation on integrating risk management and sustainability.

Ayala conducts annual risk assessments attended by senior leaders, risk owners, and risk designates.

Continuing risk management and sustainability integration
In the 2019 enterprise-wide risk assessment workshop, Ayala deliberately incorporated sustainability in risk identification and evaluation, considering the sustainability megatrends introduced to the corporation’s top and middle management from the previous year.
With a deeper understanding of the megatrends, participants identified emerging risks, such as, for instance, more typhoons and floods, presumably caused by climate change, which could interrupt business operations. Hence, climate change became a Business Resiliency risk driver.
Following this perspective, Green Financing became a mitigating measure for Funding risk. Opportunities these megatrends present across the group were also identified. For example, Green Financing, especially for business units involved in renewable energy or social enterprise, can be an additional source of funds.
To support our risk management process, other programs were also implemented, such as: the development of a common risk language that facilitates aggregating, consolidating, and reporting risks at the group level; risk maturity index assessment that benchmarks the corporation and the Ayala companies’ risk management practice with global standards every three years; risk tolerance study that aids in understanding Ayala’s capacity to absorb potential losses; and risk appetite workshop that articulates the level of risks that Ayala is prepared to accept in pursuit of its objectives.
Expanding risk appetite definition
In 2017, the Board approved the management recommended risk appetite which enumerates non-negotiable risks and sets limits for each of the drivers of four impact areas – financial, people, compliance, and reputational. In 2019, the senior management team revisited Ayala’s risk appetite which resulted in the addition of environmental impact area, capturing the Ayala group’s positive and negative impact to the environment and in broadening of the people impact by including our positive and negative impact to the community where we operate.

Ayala held the first Integrated Corporate Governance, Risk Management, and Sustainability Summit.
Technology
The Group Risk Management and Sustainability Unit continues to be innovative in the tools and methodologies it uses. It is currently exploring the utilization of a risk management information system in housing its risk universe and monitoring the corresponding mitigation plans.
With Information Security and Cyber risk as one of the top risks, the Learning and Organization Development Unit, in collaboration with the Information and Communications Technology Unit, sends out a monthly online course on cyber security that is mandated to be completed by all employees since December 2018. This is an initiative to strengthen the awareness of employees on information and cyber security threats and equip them with knowledge on how to respond to it.
Strengthening Ayala group’s risk financing strategy
Strategies in managing risks include avoidance, acceptance, mitigation, and/ or transfer of risk based on the company’s risk appetite. Companies usually employ a combination of risk strategies—mitigation and transfer. In Ayala group, the effectiveness of our risk management strategies is incorporated in the annual risk assessment process where risk owners perform their self-assessment. To provide independence, the Internal Audit reviews, on a regular basis, critical processes that mitigate top risks. Every three years, Ayala engages a third party service provider to engage senior management.
and their direct reports in a risk maturity index workshop that benchmarks our practices with global organizations.
The initial risk maturity index workshop showed that insurance portfolio optimization, risk correlation, and self-insured risk valuation were opportunity areas. Substantial work in these areas were planned and being implemented in phases. The insurance portfolio optimization was an opportunity for the group to leverage its size to improve wordings and coverage. To start on risk correlation, the initial optimized program for property damage and business interruption cover included risk management bursary, which was utilized for risk management studies such as natural catastrophe modeling, business interruption study, risk engineering survey, and asset valuation, among others. The studies elevated the group’s awareness of potential issues and addressed them by way of mitigation or risk transfer.
Ayala’s CRO saw another opportunity – elevating risk financing as a strategy as opposed to a regular transaction. This mindset change involved commitment from business units in mitigating operational risks on a daily basis, challenging retention values, and tracking of relevant data.
To institutionalize this opportunity, a risk financing strategy roadmap was laid out as a guide for continuous improvement.
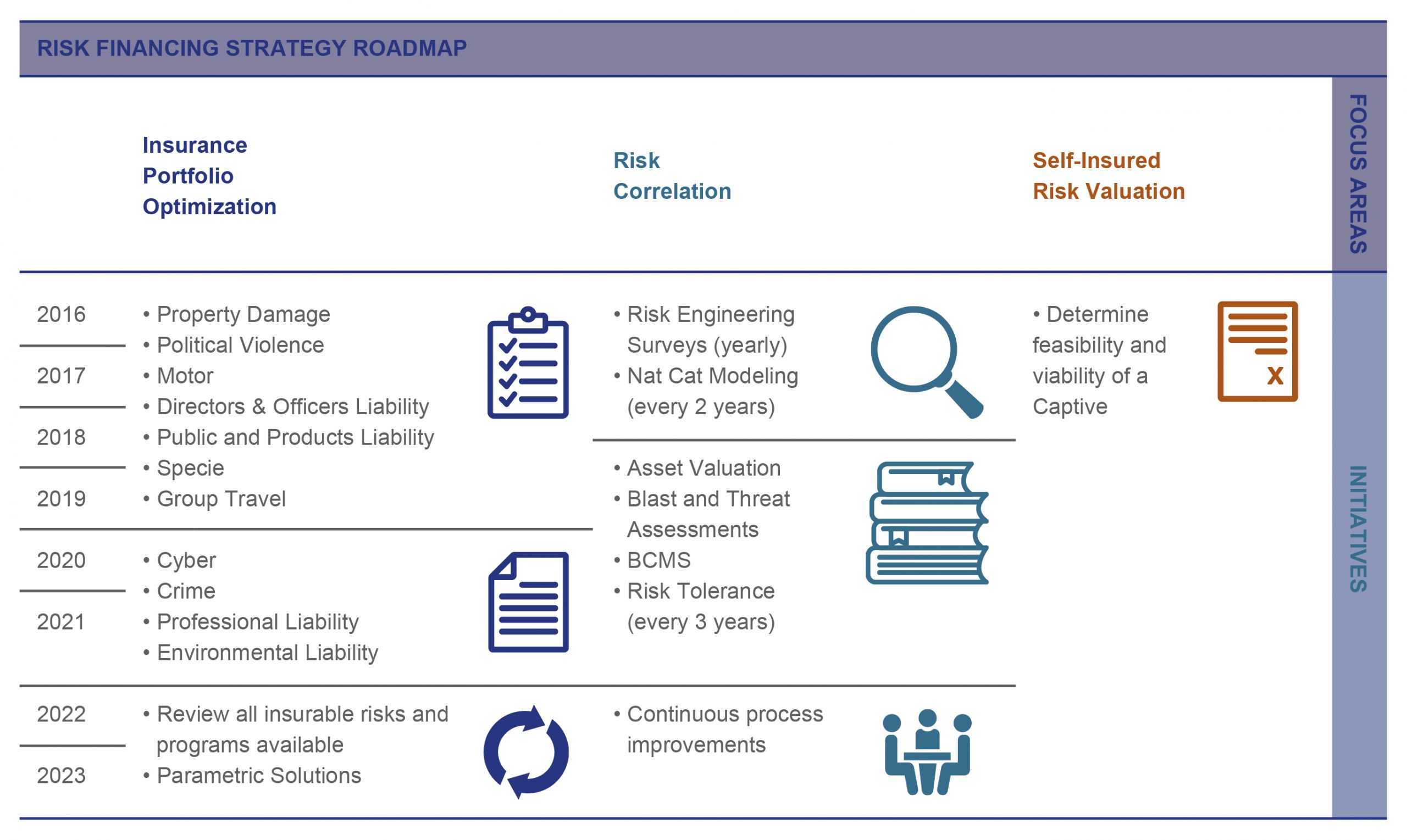
Insurance portfolio optimization
The renewal of Ayala’s optimized program for property damage and business interruption cover in the second half of 2019 was challenging, as markets were prompted to a “return to profitability” mindset. The commercial insurers started taking hits from catastrophic events—claims started to increase affecting its bottom line. Adapting to the market situation, we restructured our cover to minimize the impact while still maintaining our improved wordings and coverage achieved during the first placement.
On renewal of the optimized political violence cover, Ayala through AON negotiated for a risk management bursary—for threat and blast assessments available to business units. These studies can improve security management and potentially lower risk exposures relating to political violence.
Following the roadmap, other insurance lines are being reviewed. The review requires collection, aggregation, and consolidation of data and walk-through workshops with operating personnel to understand processes, risk exposure, and existing controls. In 2019, the Ayala group’s fine arts insurance policy was optimized. This complemented the property insurance program by providing a specific and a broad ‘nail to nail’ coverage for works of art and other collections owned by or loaned to the group.
In collaboration with Ayala group’s Human Resources teams, the group travel program, which provides employee protection during official travels was placed. Comprehensive coverage bespoke for the group was designed, which ensured consistent application and minimized potential gaps by having a program for frequent travelers as well as a ready comprehensive program for ad hoc travelers.

Risk Engineering Survey conducted by AON and insurers for our solar plants.
Risk correlation
Since 2018, various risk studies were implemented to aid management in understanding risk exposures and adequacy of cover. These studies are on a rolling three-year schedule so that all assets and scenarios can be covered and updated accordingly.
• Natural Catastrophe modeling – to understand exposure for typhoon or earthquake events
• Risk Engineering surveys – to assess probable maximum loss scenarios and to improve risks mitigation following best practice recommendations
• Asset valuations – to assess adequacy of insurable values
• Business Interruption workshops – to assess potential financial impact of work stoppage due to accidental damages and incidents
Self-insured risk valuation
Before risk transfer strategy can be implemented, the company’s risk retention capability is also evaluated by stress testing the balance sheet, understanding the frequency of loss events, and consolidating total cost of insurance premiums and related expenses. To further strengthen the risk financing strategy, Ayala is exploring the possibility of establishing a captive vehicle through a feasibility study focused on property damage and business interruption, the premium of which comprised 80 percent of the total cost of insurable risk.
With a clear risk financing strategy, Ayala can manage uncertainty, maintain liquidity, and improve total cost of risk.
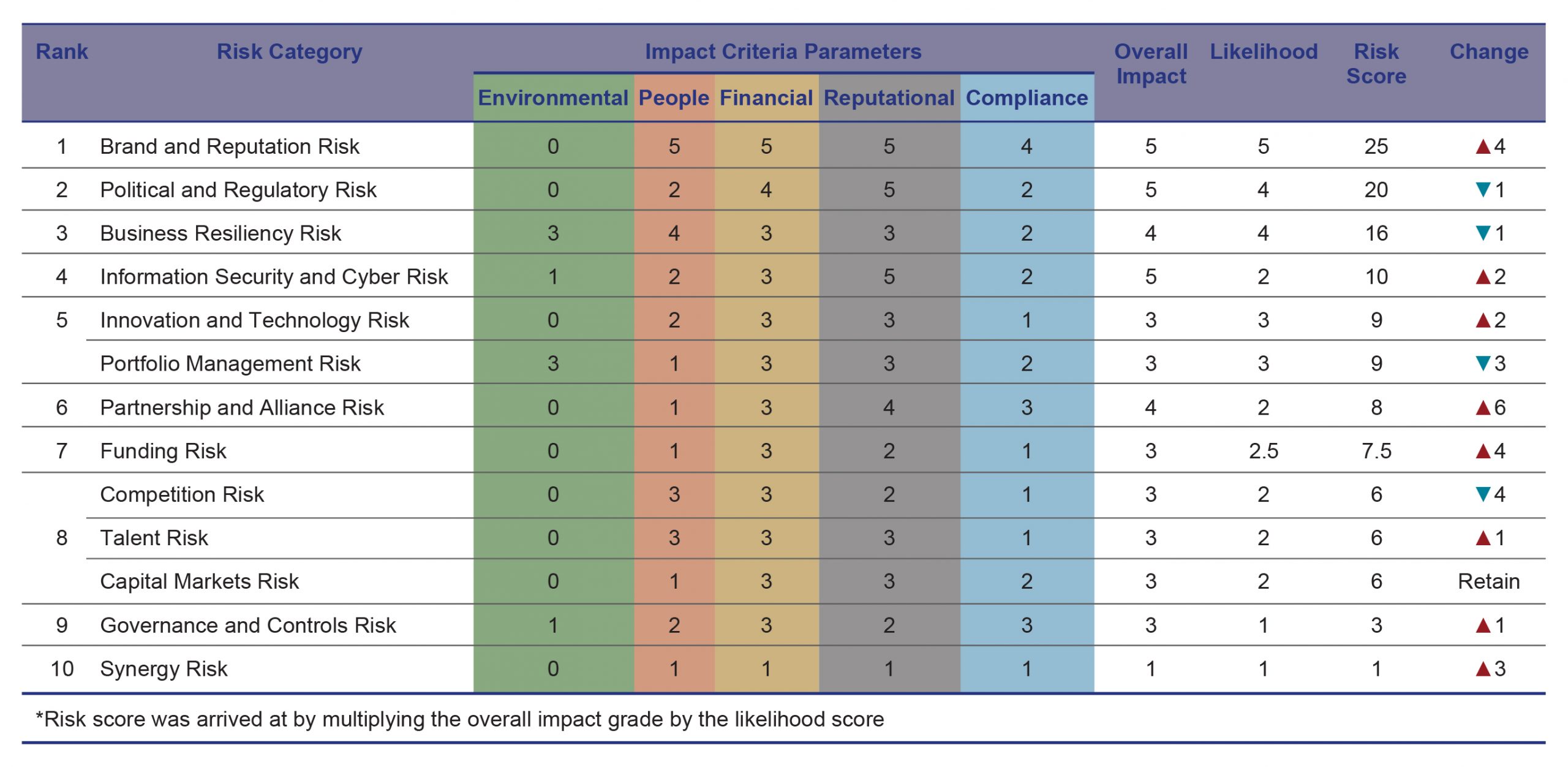
Reprioritizing risks
Participants, risk owners and risk designates, in the annual risk assessment exercise prioritized Ayala’s risks according to the impact they have on people, finance, reputation, compliance, and environment.
Aside from the likelihood and impact scores, the risk owners and risk designates also revisited the drivers of each risk category and discussed the potential implications of these risks to the corporation should it happen. More importantly, they updated their risk response plans to better mitigate the identified implications.
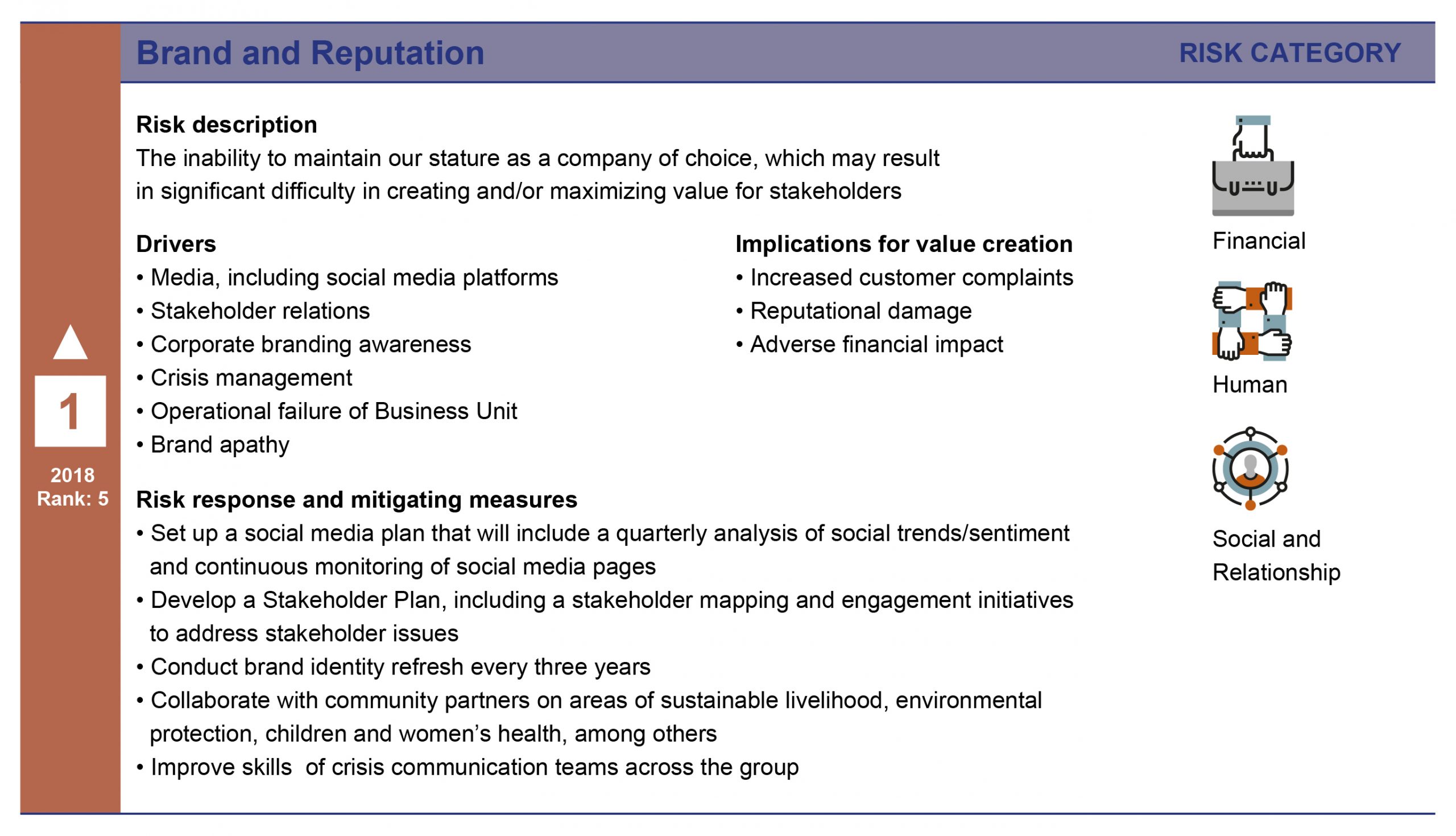
The next few pages detail the risk drivers, potential impacts, and response plans for the top five risks as of the last risk assessment workshop.
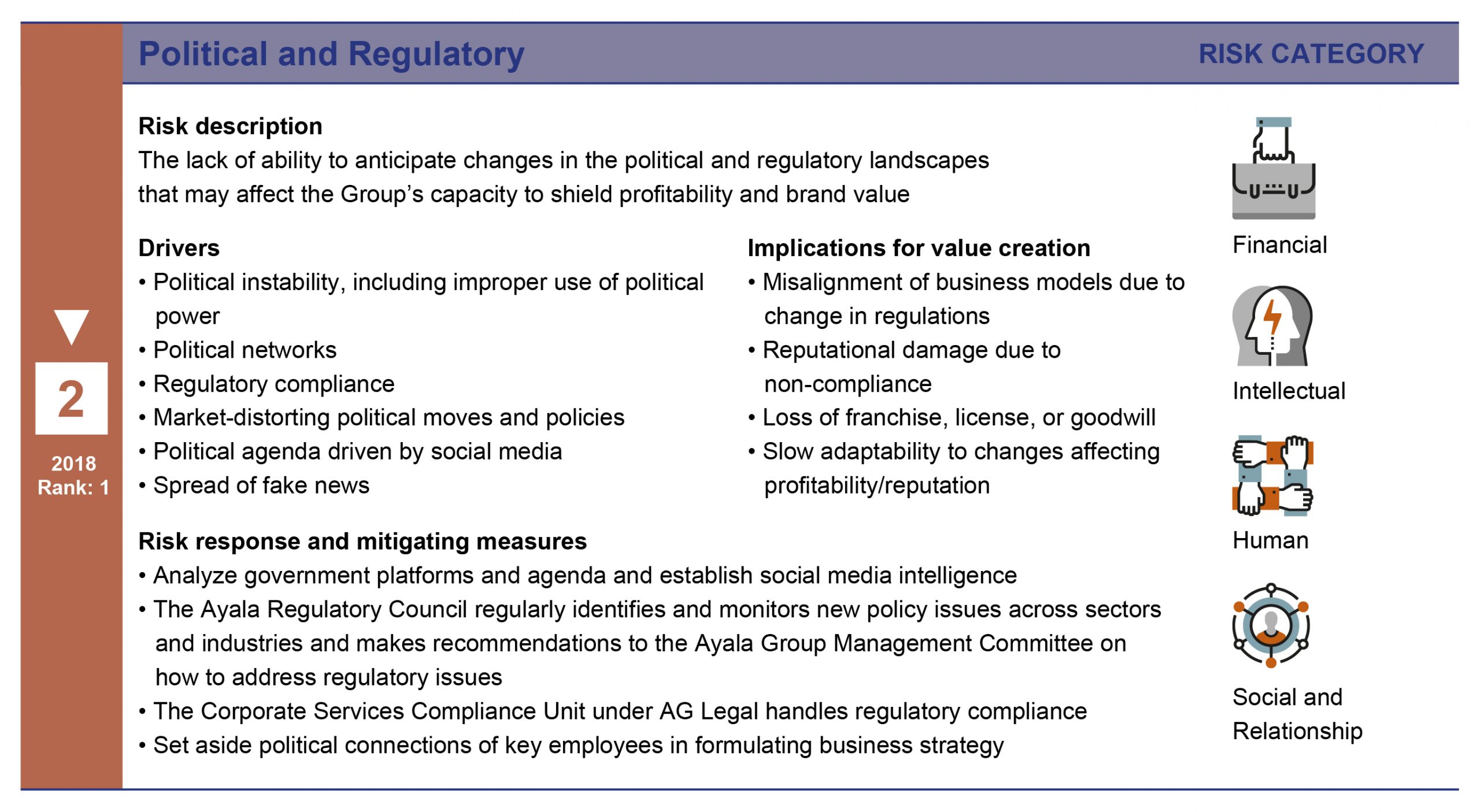


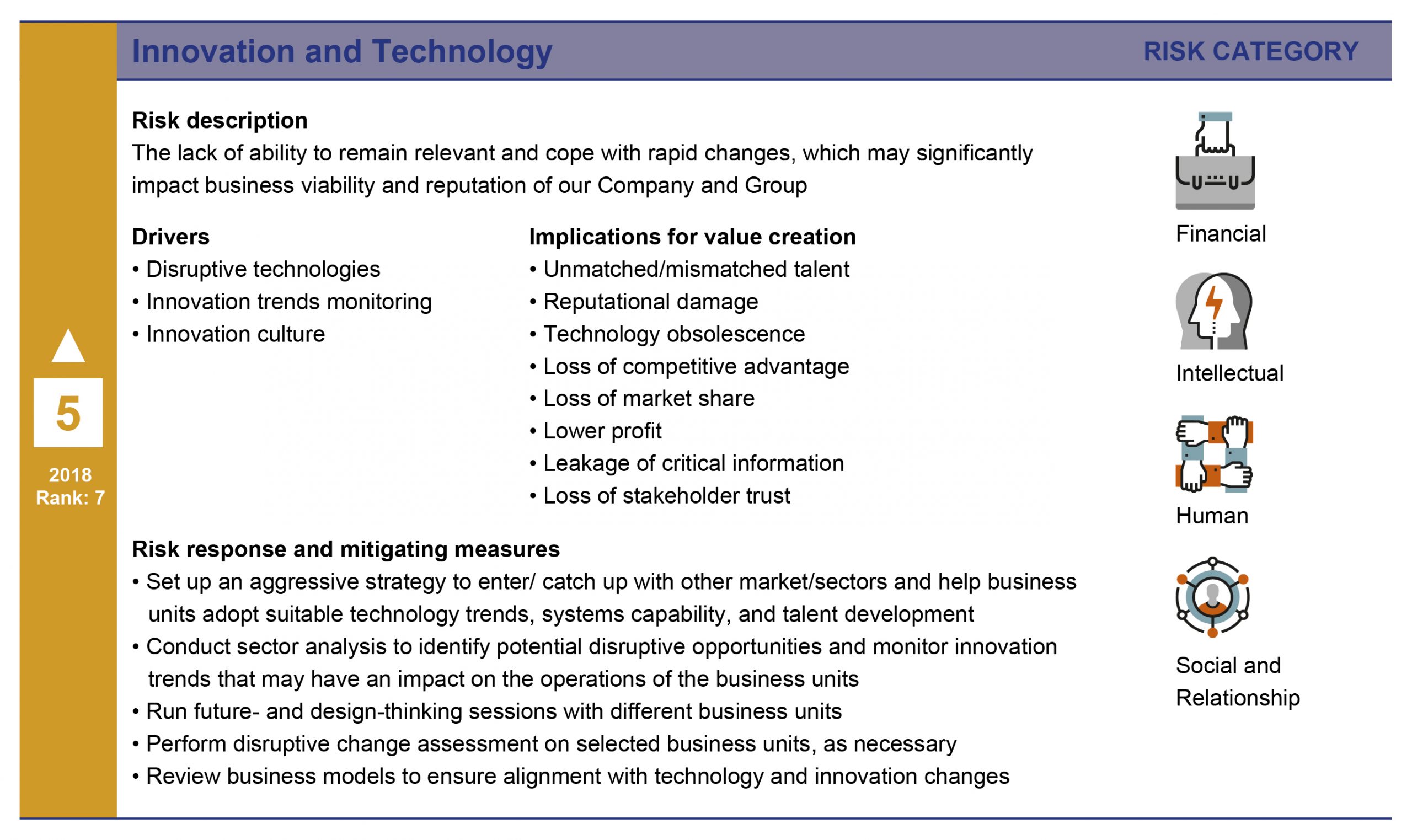
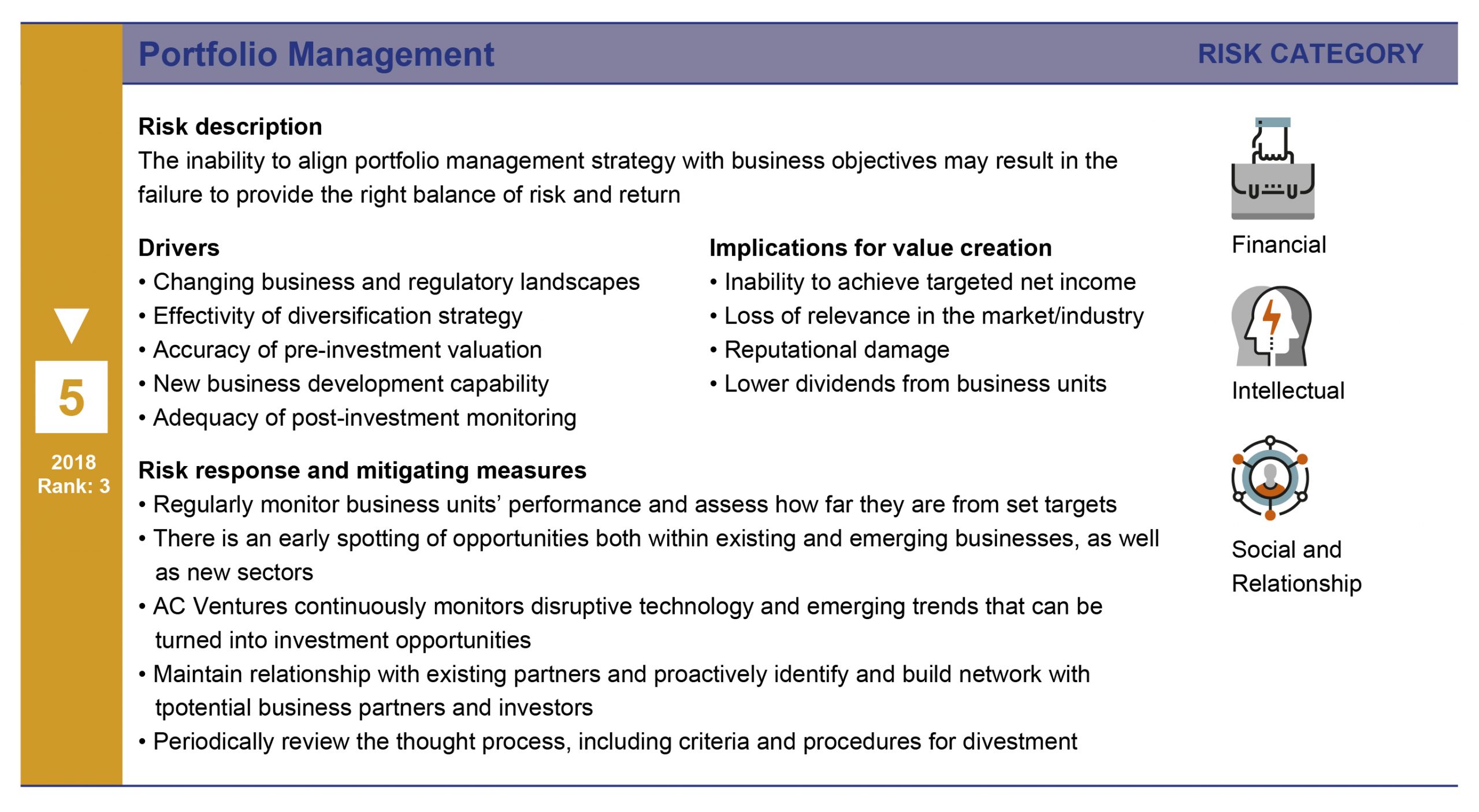
Focus on climate action through TCFD
Climate change is a defining issue of our time. The United Nations exhorts the world to act with urgency because it touches all aspects of life—environmental, societal, economic, political, regulatory, and technological. Its effect on the global economy is potentially devastating. This effect varies from one country to another. Studies show that impact is higher than the global average in Southeast Asia, one of the most complex seismic zones in the world.
The Philippines, being one of the Southeast Asian nations, is thus highly vulnerable. It stands to lose six percent of its GDP annually by 2100 if no action is taken on climate-related issues, according to a study by the Asian Development Bank. The country is expected to face an increase in extreme weather events, rising sea levels, rising temperatures, and severe rainfall. Moreover, its level of vulnerability is aggravated by its geographical location, which has high exposure to tropical cyclones and earthquakes.
The Ayala group recognizes that climate change poses risks across its business units and has long since been an advocate of environmental stewardship, ensuring that its companies and subsidiaries operate responsibly.
The Ayala group recognizes the implications of climate change:
1. Governments and businesses will have challenges in securing resources domestically and internationally;
2. Changes in food, water, and energy patterns could lead to increased conflict over resources and eventually lead to political tension;
3. As disputes over resources heighten, national survival will be more critical and will undoubtedly lead to potential regional or international confrontations over water, oil, fishing, and other mineral rights;
4. The lack of resources and increasing climate change impacts could force existing industries to be revolutionized or could pave the way for new ones. These changes will be accelerated by innovation and technology, and nations must ensure that the workforce is not displaced; and
5. There will be increased levels of regulations, both directly on environmental changes and indirectly through taxation and similar types of incentives/disincentives.
With these climate change implications in mind, Ayala promotes a risk-aware culture and recognizes the climate-related risks classified by the Task Force for Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) into two types:
Transition risks are controlled and have lower economic damage, but pose aggressive change. Their initial impact can be severe but reduces over time. In contrast, physical risks have higher economic damage and cause accelerated change. Their initial impact may or may not be severe, but it definitely increases over time. Ayala believes that such risks can be turned into opportunities if preemptive action is taken.
With the results of the Natural Catastophe modeling undertaken out of the risk management bursary in May 2019, Ayala was able to determine the potential financial impact of such calamities to its businesses. The modeling used common return periods of 250 years for earthquake and 200 years for typhoon, considered top historical events like typhoon Haiyan, and included worst case scenarios. The results yielded the following:
a. For earthquake: 250-year Ayala group modeling loss is about US$591 million
b. For typhoon: 200-year Ayala group modeling loss is about US$278 million
Climate change has been identified as a risk driver of Business Resiliency Risk, one of the top five risks of Ayala Corporation in the last three years. The importance given by Ayala’s business units to the environment and their awareness of the impact of climate change is notable.
In responding to the call for a more effective climate-related financial reporting, Ayala set off its voluntary disclosures guided by the Task Force for Climate-related Financial Disclosures standards. Focus was given to four key pillars—governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics and targets—with 11 widely adoptable recommendations that consider the physical and transition risks associated with climate change.
Results of the initial phase taken by Ayala show its strength in its GHG emissions disclosures. It has eight disclosure areas that are present and needs significant enhancing, and two disclosure areas for development.
To obtain these results, Ayala’s performance was assessed against the four key pillars and their disclosures. The process included public resource reviews, management-level interviews, and a gap assessment.
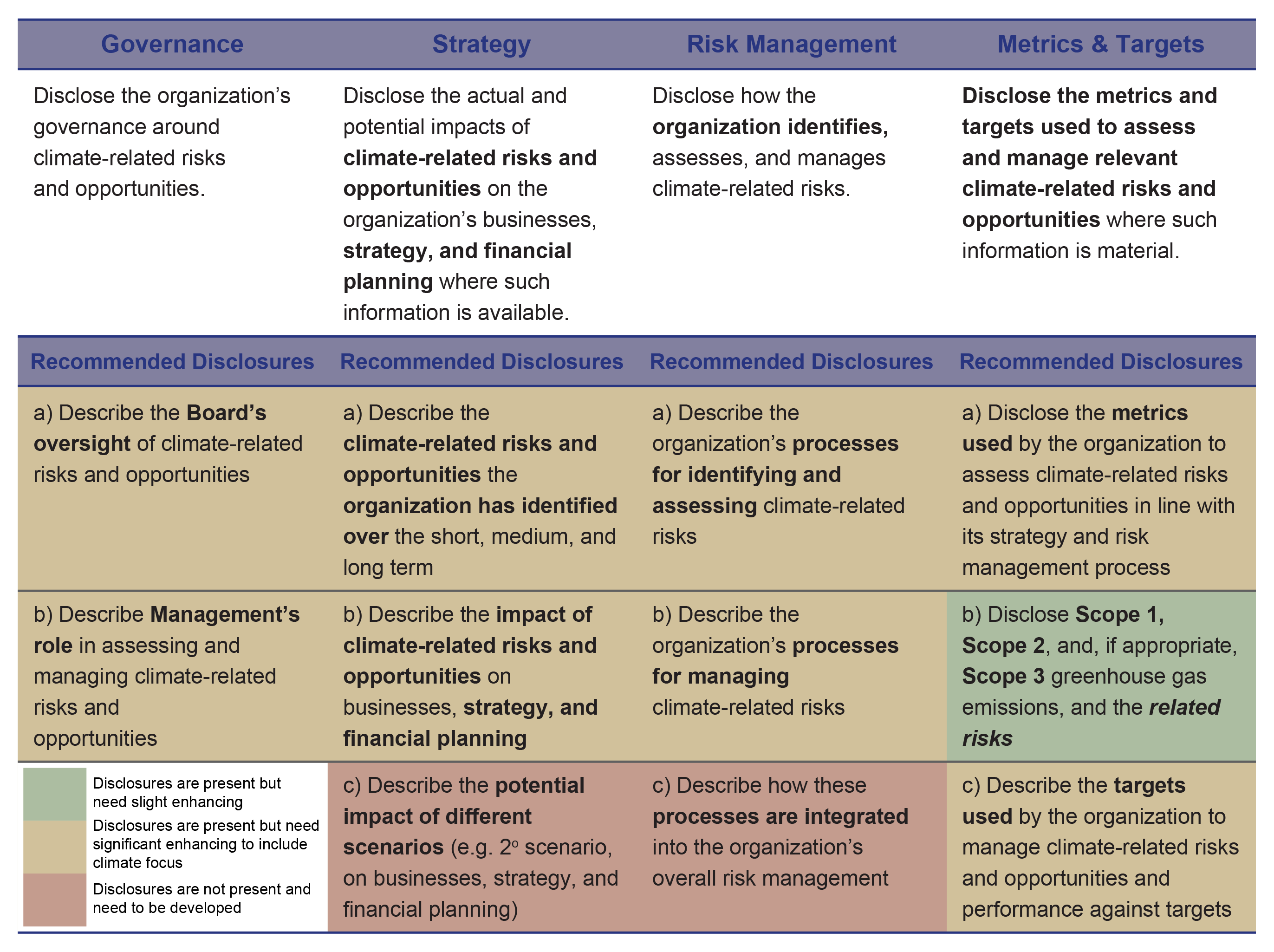
Current State Assessment of Ayala

The first phase of the TCFD journey paved the way for Ayala to include climate-related risks and opportunities in the upcoming 2020 risk assessment exercise. It has prepared the group for future actions that involves boardroom education and transition strategy, risk and opportunity mapping, and reporting and communication. These actions are aimed at ensuring the company meets all 11 disclosures of the TCFD recommendations.
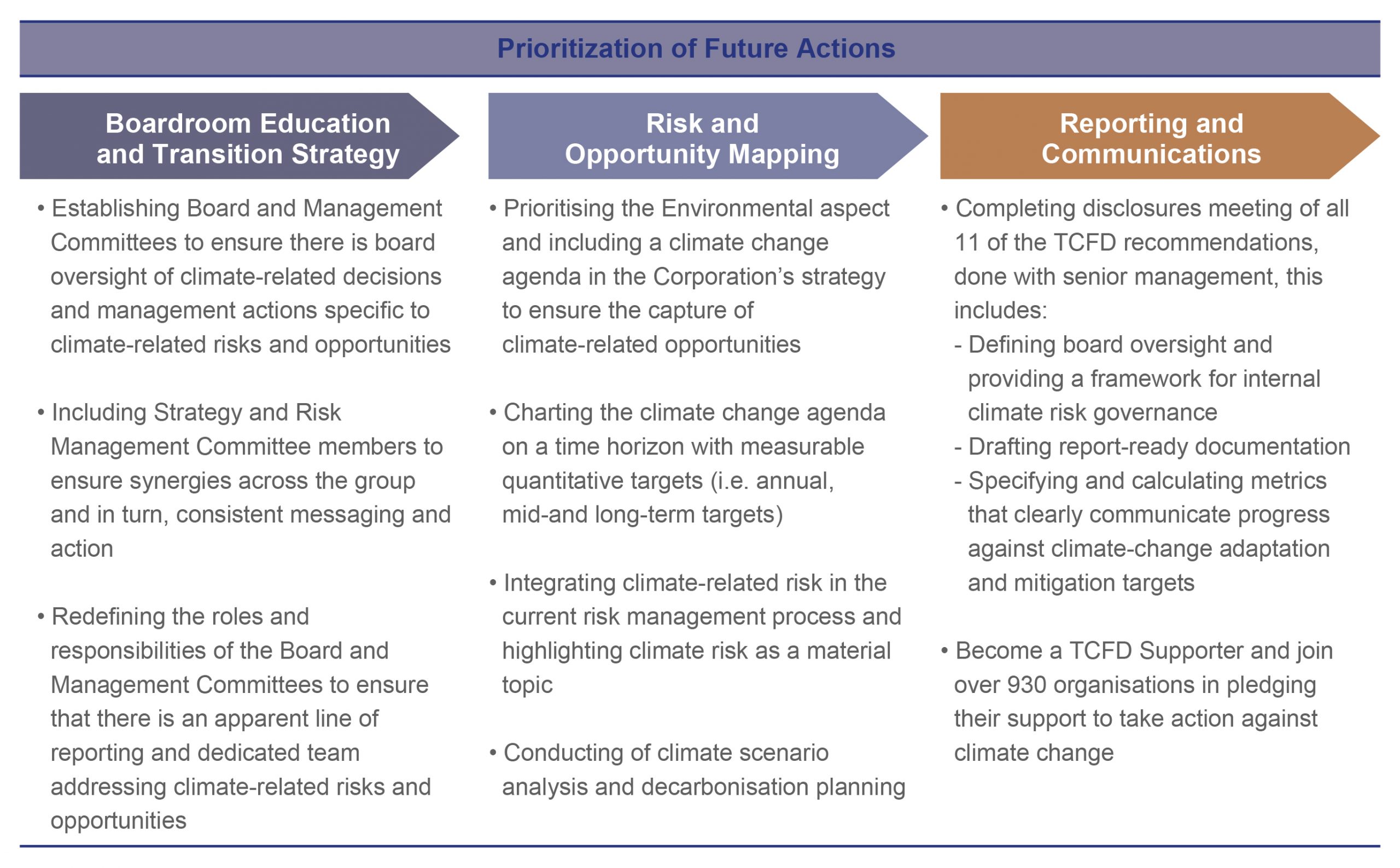
Ayala extends its efforts to bring all its business units on board and united in going beyond the bottom line. As it sets its eyes on the goal to draft report-ready documentation, Ayala commits to be a TCFD Supporter, ensuring that our declarations come with tangible results with a meaningful impact.





